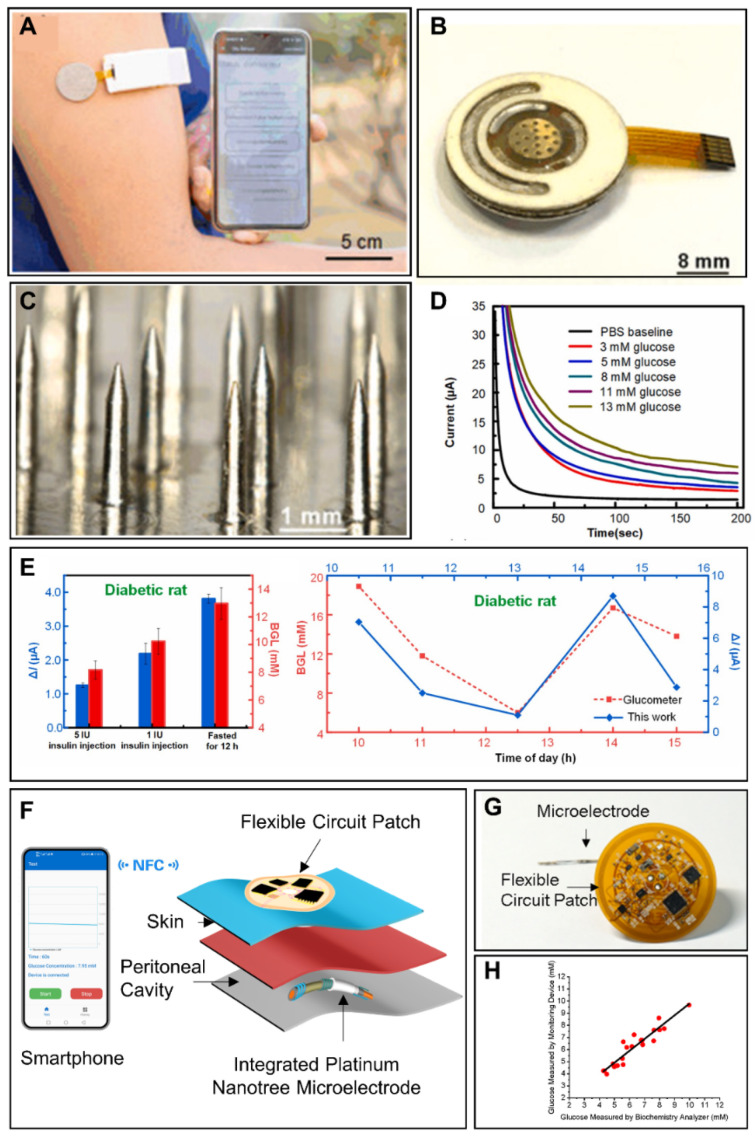
Figure 4.
Smartphone-based implantable glucose monitoring. (A) Smartphone-based ISF glucose analysis with microneedle array. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [106] Copyright (2022) Elsevier. (B) Photograph of an ISF glucose sensor. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [106] Copyright (2022) Elsevier. (C) Optical photo of a microneedle array. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [106] Copyright (2022) Elsevier. (D) The chronoamperometric responses of a glucose sensor under subdermal glucose concentrations of 3–13 mM. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [106] Copyright (2022) Elsevier. (E) In vivo glucose sensing performance of the smartphone-based ISF glucose analysis system in diabetic rats. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [106] Copyright (2022) Elsevier. (F) Schematic diagram of implantable ascitic glucose monitoring system. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [42] Copyright (2021) Elsevier. (G) Optical image of integrated platinum nanotree microelectrode and a flexible circuit patch. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [42] Copyright (2021) Elsevier. (H) Comparison between glucose concentrations measured by a smartphone-based ascitic glucose monitoring system and a biochemical analyzer. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [42] Copyright (2021) Elsevier.