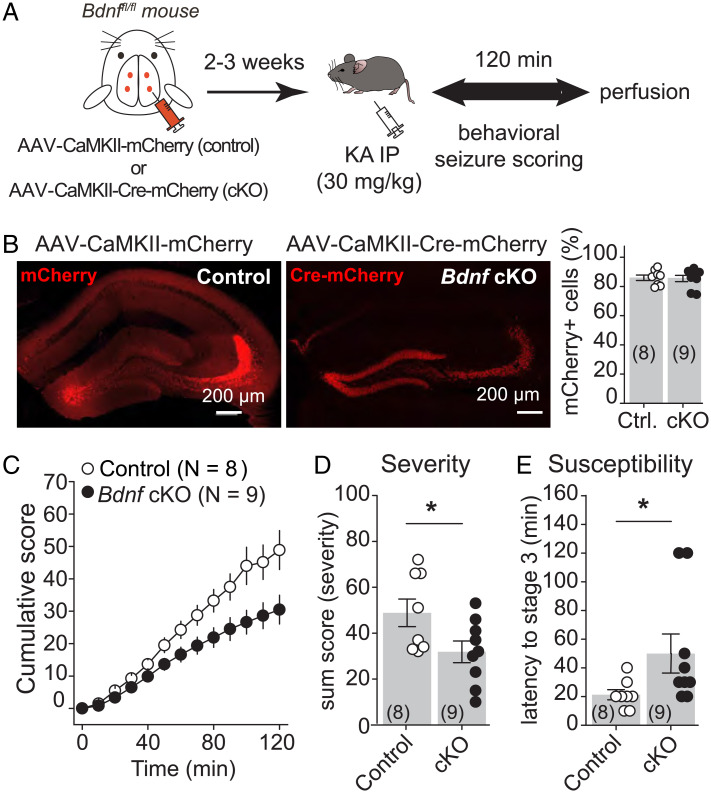
Fig. 5.
Knocking out BDNF from hippocampal excitatory neurons reduced KA-induced seizures. (A) AAV-CaMKII-mCherry (control) or AAV-CaMKII-Cre-mCherry (cKO) was injected bilaterally into ventral and dorsal DG of Bdnffl/fl mice. (B) Representative confocal images (Left) and quantification (Right) showing high viral expression in the DG. Control (Ctrl) vs cKO. (C–E) Deletion of BDNF from hippocampal excitatory neurons (Bdnffl/fl mice injected with AAV-CaMKII-Cre-mCherry) induced significant decreases in the cumulative seizure score (C) and in the sum score (D) and a significantly increase in latency to convulsive seizures (E) as compared with controls (Bdnffl/fl mice injected with AAV-CaMKII-mCherry). *P < 0.05. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.