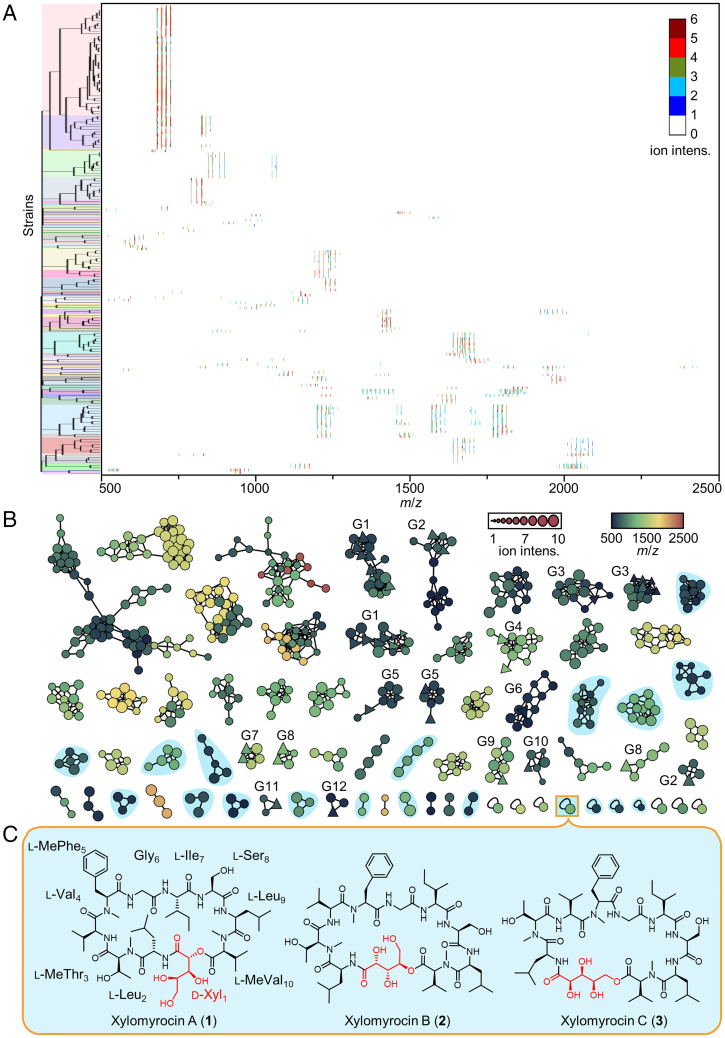
Fig. 1.
MS-guided chemometric discovery of polyol cyclodepsipeptides. (A) Hierarchical clustering of the MALDI-TOF MS spectra of SM extracts from 182 fungal isolates (SI Appendix, Table S1). The resulting 61 clades are highlighted by different colors on the tree. The heat map shows the MS fingerprints of the extracts. The gradient color indicates the intensity (intens.) of each ion signal. (B) Molecular network analysis of the peptide SMs, based on the LC-HRMS/MS fingerprints of metabolite extracts from fermentations with 61 fungal strains, exemplifying the 61 clades identified in A. Each node represents the parent ion of one single peptide. The shape of the node indicates whether the MS/MS spectrum of the peptide has a GNPS database hit (triangle, known peptide; circle, unknown peptide). The size and color of the node indicates the MS intensity and the m/z of the parent ion, respectively. Peptides with similar MS/MS spectra are connected by edges and form a clade. The length of the edge indicates the structural similarity between two peptides. Clades labeled as G1–G12 contain putative analogs of SMs with known structures (G1: enniatins and bassianolides; G2: beauvericins; G3: hormonemates; G4: acremostatins; G5: arenamide A and emericellamide A; G6: communesin B; G7: GNPS spectrum ID CCMSLIB00000001578 and CCMSLIB00000001580; G8: cyclosporins; G9: trikoningin-KB-I; G10: ferrichrome; G11: GNPS spectrum ID CCMSLIB00000853575; G12: 27-epi-tryptoquivaline); those highlighted in cyan indicate putative novel cyclic peptides, collectively produced by 10 representative fungal strains. [M+H]+ and [M+NH4]+ adducts of the same peptide tend to group together to form one cluster, while [M+Na]+ adducts of the same peptide routinely form a separate cluster. (C) The chemical structures of xylomyrocins A–C (1–3), polyol cyclodepsipeptides isolated from Paramyrothecium sp. XJ0827. d-Xyl, d-xylonic acid; l-Leu, l-leucine; l-MeThr, N-methyl- l-threonine; l-Val, l-valine; l-MePhe, N-methyl- l-phenylalanine; Gly, glycine; l-Ile, l-isoleucine; l-Ser, l-serine; l-MeVal, N-methyl- l-valine.