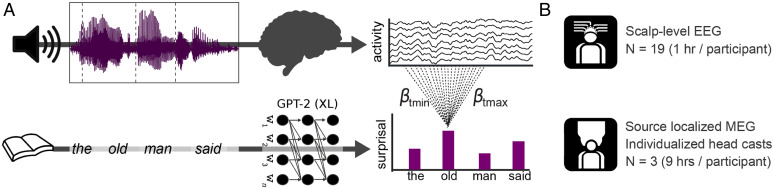
Fig. 1.
Schematic of experimental and analytical framework. (A) (Top) In both experiments, participants listened to continuous recordings from audiobooks while brain activity was recorded. (Bottom) The texts participants listened to were analyzed by a deep neural network (GPT-2) to quantify the contextual probability of each word. A regression-based technique was used to estimate the effects of (different levels of) linguistic unexpectedness on the evoked responses within the continuous recordings. (B) Datasets analyzed: one group-level EEG dataset, and one individual subject source-localized MEG dataset.