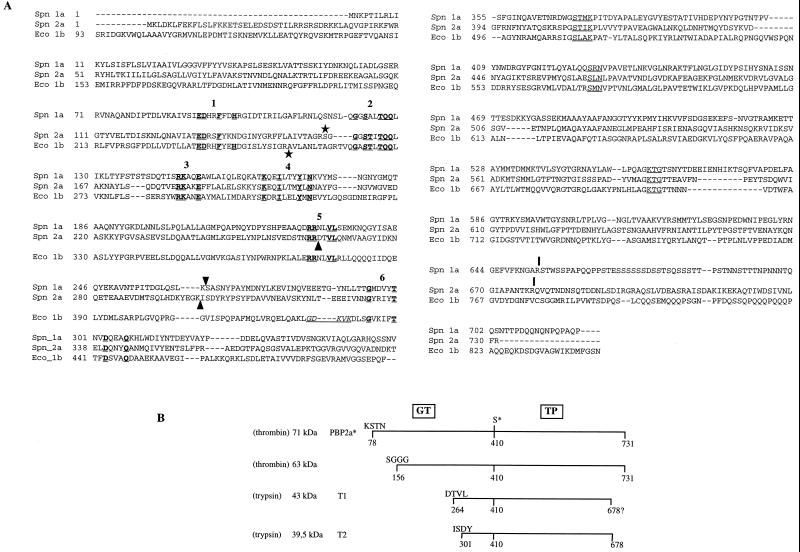
FIG. 1.
(A) Alignment sequence of class A high-Mr PBPs S. pneumoniae PBP 1a, PBP 2a (11, 12), and E. coli PBP 1b. The conserved motifs in the GT domain are underlined and in boldface, and are numbered according to the system used in reference 8. The active-site conserved motifs in the TP domain are underlined. Arrowheads indicate the N-terminal positions of the PBP 1a TP domain (Ser 264) (3) and T1 and T2 tryptic products of PBP 2a (this work). The underlined residues in italics correspond to the permissive site found in E. coli PBP 1b delineating the GT and TP junction domains (16). Vertical bars indicate the C terminus of TP domains (reference 3 and this work). Stars indicate the first residue of the detergent-free soluble proteins (reference 26 and this work). (B) Schematic representation of the proteolytic fragments. The molecular mass of each fragment was measured by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal sequence of the fragments was experimentally determined. The C terminus of T2 is derived from mass spectrometry measurements. The position of the active-site serine 410 is indicated (S*).