Figure 3.
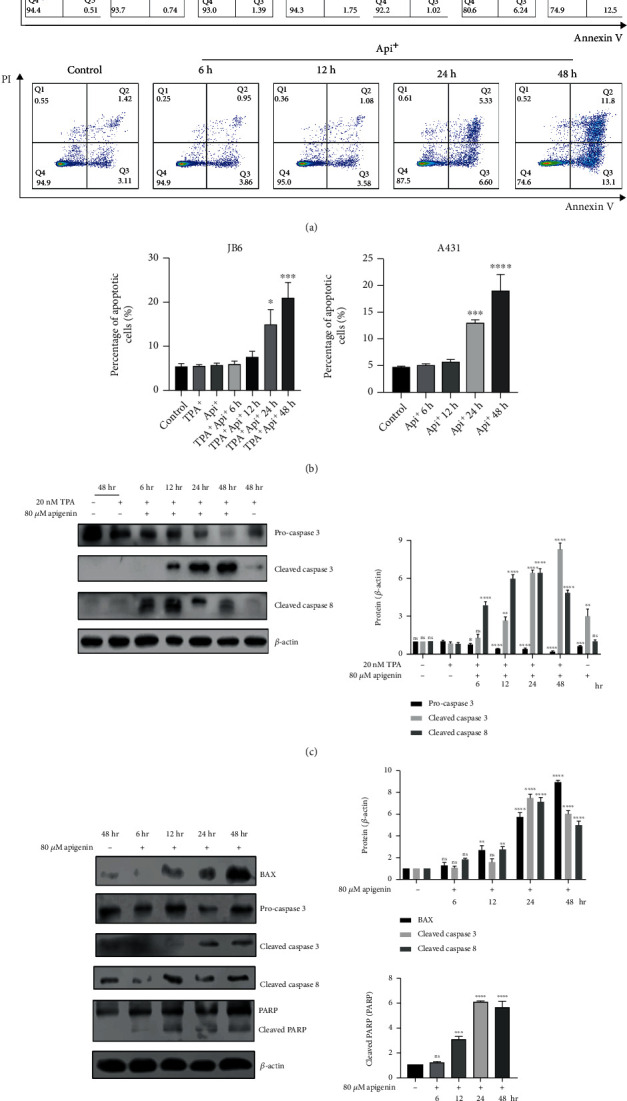
Apigenin induced apoptosis in cSCC cells. (a) Flow cytometry was used to analyze the apoptosis cells. Cells were stained with annexin V and PI to quantify the percentage of apoptotic cells. TPA-induced JB6 cells (upper) or A431 cells (lower) were treated with control (DMSO) or 80 μM apigenin for different times. (b) A concrete percentage of apoptosis cells in TPA-induced JB6 and A431 cells were evaluated using a one-way ANOVA (mean values ± SEM, n = 3) ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001vs. control (TPA-induced sample as control for JB6 cells). (c) TPA-induced JB6 cells were incubated with control (DMSO) or 80 μM apigenin for 6 h-48 h. Western blot was served to analyze the expression of apoptosis-associated proteins (left). The bar graphs on the right showed the intensity of the protein band from each treatment relative to the housekeeping protein (β-actin). Valued represent the means ± SEM. Significant difference was designed by ANOVA, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001vs. control (only TPA-induced sample). (d) The apoptosis-associated proteins were detected while 80 μM apigenin was used for treatment for different time-points in A431 cells. The bar graphs showed the intensity quantification of the protein band relative to the housekeeping protein. Significant difference from control by ANOVA, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
