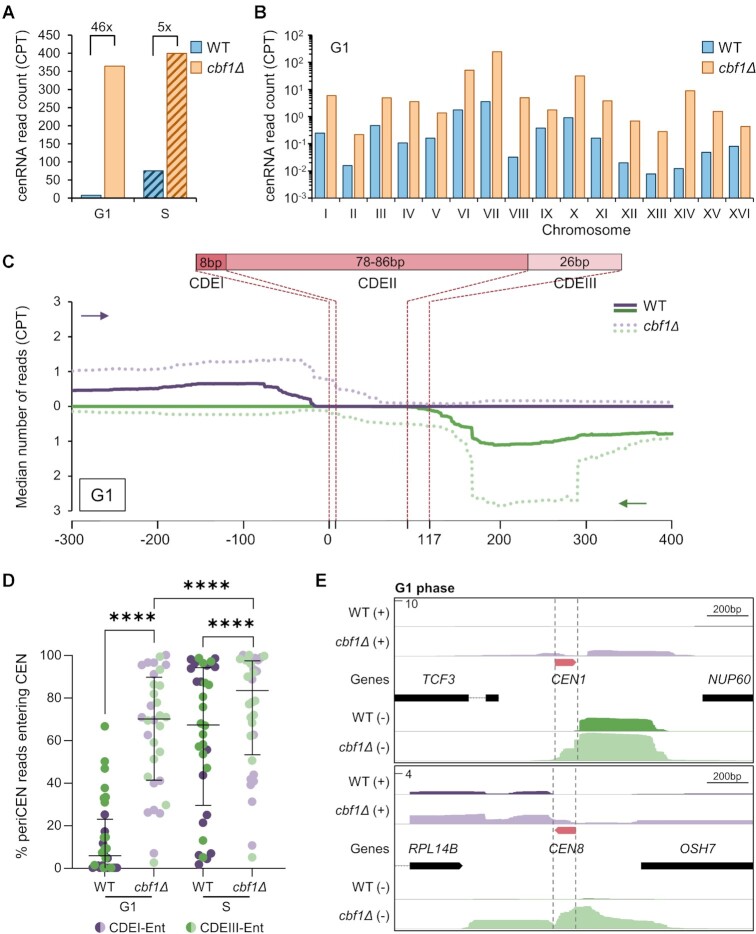
Figure 3.
Cbf1 negatively regulates cenRNA expression and promotes transcription termination at the CEN border in G1. (A) Total number of normalized cenRNA read counts measured in counts per thousand (CPT) after hybridization capture enrichment. (B) Distribution of normalized cenRNA read counts per chromosome. (C) Aggregate plot of median read count around centromeres. All 16 centromeres, regardless of the strand of origin, have been aligned at the beginning of the CDEI element (top plot) or the beginning of the CDEIII element (bottom plot). The 5′–3′ direction is indicated by a purple arrow for reads converging toward the CDEI element and a green arrow for reads converging towards the CDEIII element. The structure of the centromere is schematically shown on the top. (D) Distribution of the proportion of pericenRNA reads that enter the CEN. Each centromere is represented by two dots, for reads coming from each strand. Median plus interquartile range is displayed in black. P-values determined by a paired Wilcoxon test (****P < 0.0001). (E) Example of Iso-Seq profiles at CEN1 and CEN8 in G1 for WT and cbf1Δ cells. Position of centromere boundaries is shown by the vertical grey dotted lines. Reads coming from the (+) strand are shown in purple while reads coming from the (–) strand are shown in green. The y-axis represents the maximum CPT. All WT data are copied from Figure 2 and shown for comparison purposes.