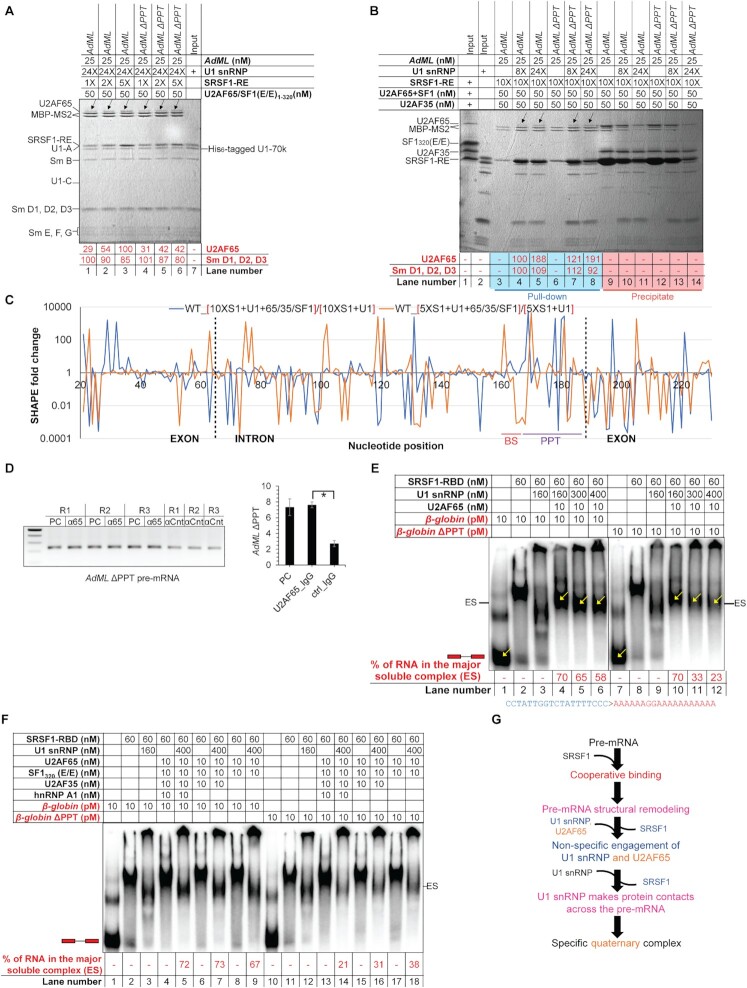
Figure 5.
Specific U2AF65 recruitment requires cooperative binding and displacement of SRSF1. (A) Amylose pull-down assay showing binding of increasing levels of U2AF65 with increasing SRSF1-RE:AdML ratio but fixed U1 snRNP:AdML ratio; black arrows mark the U2AF65 bands; band intensities normalized to the MBP-MS2 levels are shown; a background-subtracted and contrasted version of this image is shown in Supplementary Figure S5A. (B) Amylose pull-down of AdML in the presence of 8× or 24× molar excess U1 snRNP, 10× molar excess of SRSF1-RE, and 50 nM [U2AF65 + SF1320 (E/E) + U2AF35]. (C) Fold changes in SHAPE reactivity upon addition of [U2AF65 + SF1320 (E/E) + U2AF35] to [AdML + 24× U1 snRNP + 10× SRSF1-RE] (blue line) and to [AdML + 24× U1 snRNP + 5× SRSF1-RE] (orange line); exon-intron boundaries are demarcated with dotted vertical lines and the BS and the PPT regions are marked. (D) (Left) Amplification of AdML ΔPPT pre-mRNA by RT PCR from pre-cleared extract (50 μg total protein, PC), immunoprecipitant obtained from the pre-cleared extract (500 μg total protein) with anti-U2AF65 antibody (α65), and immunoprecipitant obtained from uncleared extract (500 μg total protein) with IgG2b control antibody (αCnt) performed in triplicate; (right) a plot showing significant enrichment of AdML ΔPPT with anti-U2AF65 antibody compared to the control antibody; error bars indicate standard deviation, ‘*’ P < 0.05, n = 3. (E) EMSA showing titration of the quaternary complexes of β-globin WT and β-globin ΔPPT assembled with SRSF1-RBD, U1 snRNP, and U2AF65 with additional U1 snRNP reduces the major soluble complex labeled as ‘ES’; the ratios of the band-intensity of the free pre-mRNA and the quaternary complexes (marked with yellow arrows inside the gel and as ‘ES’ on the side of the gel) are indicated in red script below the image; the mutated sequence in ΔPPT is shown. (F) Addition of hnRNP A1, U2AF35 and SF1320 (E/E) promotes PPT-dependent complexes for the WT substrate and but not the PPT mutant. (G) Summary flow chart: Cooperative binding of SRSF1 is critical for U2AF65 recruitment; however, U2AF65 non-specifically engages the pre-mRNA prior to displacement of some of the SRSF1 molecules by excess U1 snRNP; specific interactions between the pre-mRNA and U2AF65 are established upon displacement of these SRSF1 molecules; orange text indicates the steps added based on the conclusions of this figure.