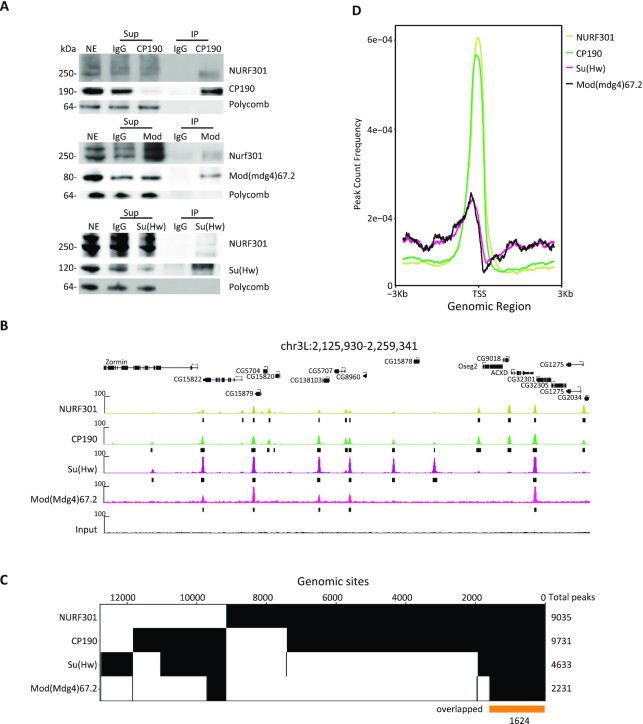
Figure 3.
NURF301 interacts physically with gypsy insulator proteins, and these factors co-localize genome-wide. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation of NURF301 with core gypsy components. Nuclear extracts (NE) are from embryos aged 0–24 h collected at RT, which is the same material used for IP followed by mass spectrometry. NE was immunoprecipitated with each antibody or with normal serum (IgG) as indicated. Unbound supernatant (Sup) and bound (IP) fractions are also shown. Polycomb (Pc) is used as a negative control. (B) Representative screenshot of ChIP-seq profiles shows NURF301 co-localizes extensively with gypsy core components in Kc cells grown at 25°C. Peaks called by MACS2 are indicated by black bars. Three biological replicates were examined for each sample. (C) Binary heatmap of CP190, NURF301, Su(Hw), and Mod(mdg4)67.2 binding sites in Kc cells, ordered by supervised hierarchical clustering. Each column represents a single independent genomic location, and a mark in a row indicates presence of the indicated factor. Total peaks of each factor are shown on the right. 7423 genomic sites co-localize between NURF301 and CP190, and 1624 genomic sites (yellow bar) were bound by all four factors. (D) Average signals of CP190 and NURF301 peaks, but not of Su(Hw) and Mod(mdg4)67.2, accumulate at the TSS.