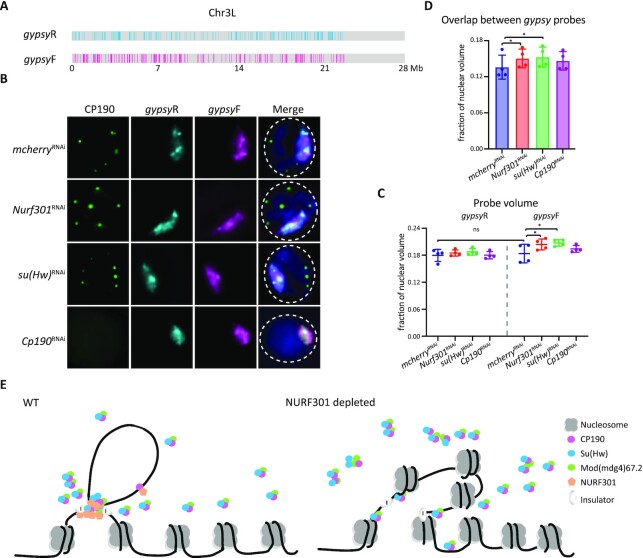
Figure 7.
Depletion of NURF301 specifically alters 3D arrangement of gypsy insulator binding sites. (A) Schematic of gypsy probes on Chr3L. The co-occupied sites of Su(Hw)/CP190/Mod(mdg4)67.2 are designated as gypsyF probe, and the 1D reverse of non-gypsy sites are designated as control probe (gypsyR). The DNA amount labeled by gypsyF or gypsyR paint is ∼5 Mb. (B) Representative images of CP190 IF and signals of gypsyF and gypsyR probes in dsRNA treated Kc cells. Cells were cultured at 25°C. Images are maximal projections of 26 Z-stacks. Nuclear edge is indicated with dashed line. Scale bar: 2 μm. (C) Probe volume relative to the fraction of nuclear volume. Left panel is control gypsyR probe, right is gypsyF probe. (D) Intermixing volume of gypsyF and gypsyR paints relative to nuclear volume. Data are from four biological replicates and a dot represents each replicate, n > 300 cells in each sample. Paired t-test was used, and error bars show standard deviation. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05 as indicated. (E) Nucleosome remodeller NURF301 cooperates with Su(Hw) to promote stable insulator complex binding at gypsy insulator sites to establish higher-order chromatin structure. After depletion of NURF301, Su(Hw) and CP190 cannot properly bind to gypsy binding sites, thus impairing gypsy insulator function and influencing chromatin organization.