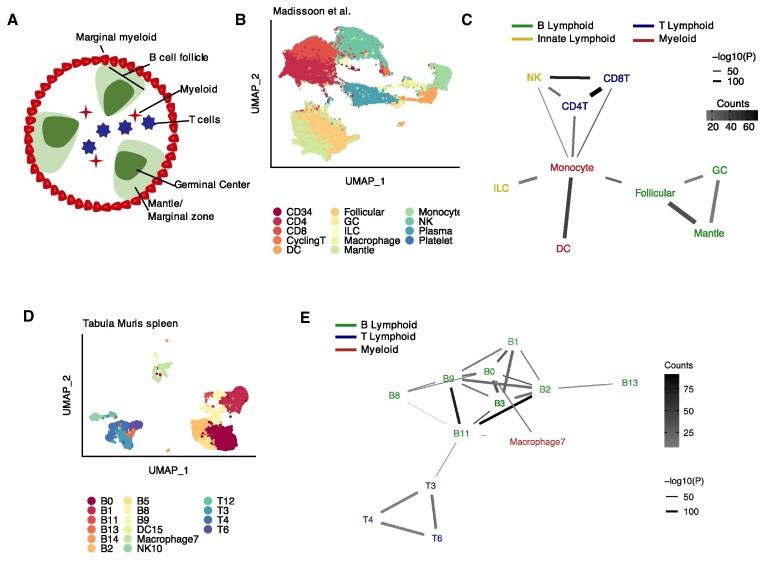
Figure 4.
Detecting known microanatomical features of the splenic white pulp. (A) Illustration of the main cell types in the splenic white pulp. (B) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) of 94 050 splenic white pulp immune cells (23) (n = 19 human samples) colored by cell type. DC, dendritic cell; GC, germinal center; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; NK, natural killer cell. (C) Network diagram of significant cell type interactions from (B) identified by Neighbor-seq, colored by known cell type lineage. Data is shown for n = 10 iterations, mean counts >5, combined P-value < 0.05. (D) UMAP of 9552 murine immune cells from Tabula Muris (24) colored by cell type. (E) Network diagram of significant cell type interactions from (D) identified by Neighbor-seq, colored by known cell compartment. Methods, edge color and thickness, and colors scale are the same as in (C).