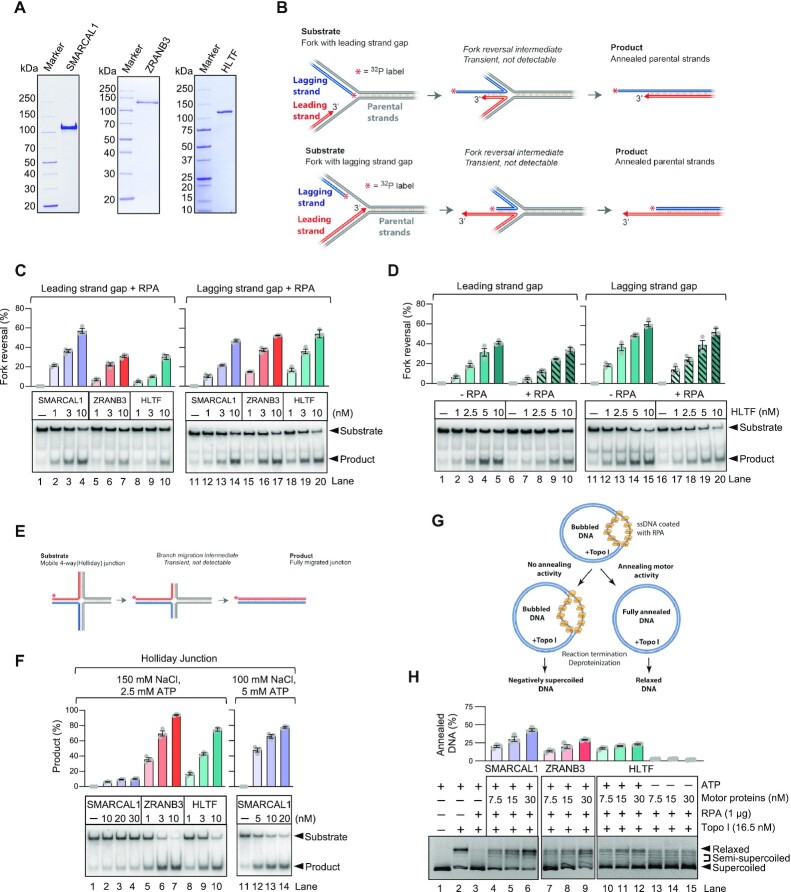
Figure 1.
SMARCAL1, ZRANB3 and HLTF possess distinct biochemical activities. (A) Recombinant SMARCAL1, ZRANB3, and HLTF were analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (B) A schematic of replication fork reversal assay (leading and lagging strand gap structure is shown). (C) Fork reversal assays with SMARCAL1, ZRANB3 and HLTF with RPA (3 nM). Top, quantifications (error bars show SEM of three replicates); bottom, representative experiments. (D) Fork reversal assays with HLTF without or with RPA (3 nM). Top, quantifications (error bars indicate SEM of three replicates); bottom, representative experiments. (E) A schematic of Holliday junction branch migration assay. (F) Holliday junction branch migrations assay with SMARCAL1, ZRANB3 and HLTF. Top, quantifications (error bars indicate SEM of three replicates); bottom, representative experiments. (G) A schematic of topoisomerase-coupled annealing assay. (H) Comparison of SMARCAL1, ZRANB3 and HLTF in topoisomerase-coupled annealing assays. ATP hydrolysis by HLTF is required, as no detectable annealing was observed without ATP. Top, quantifications (error bars indicate SEM of three replicates); bottom, representative experiments.