Figure 2.
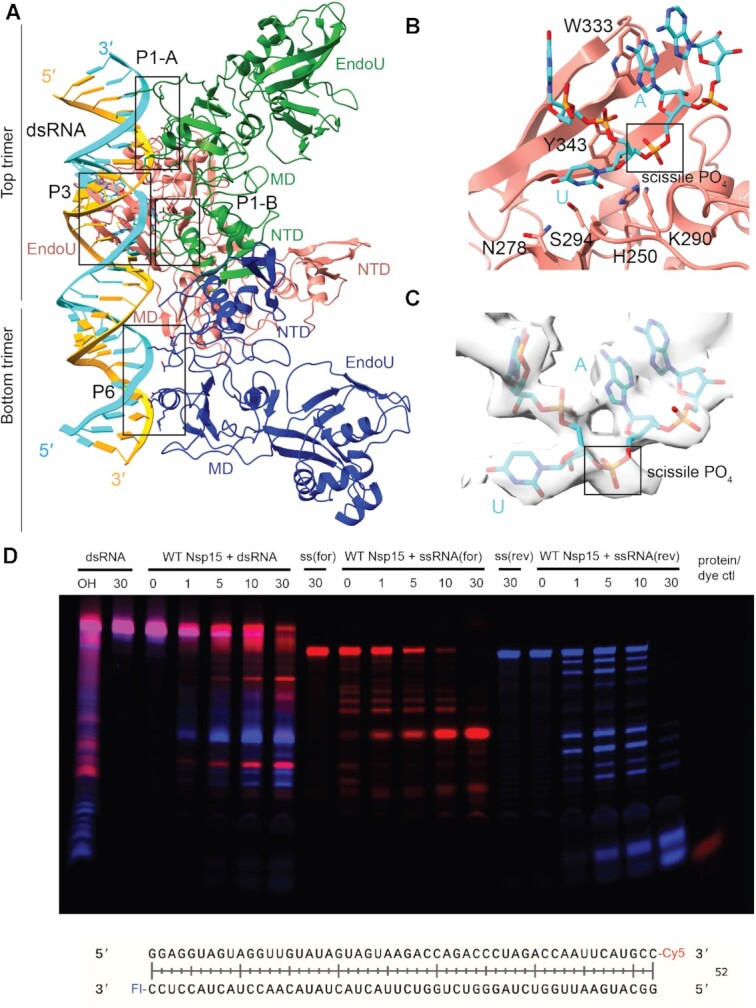
Nsp15 can cleave both ss- and dsRNA. (A) DsRNA interacts with three Nsp15 protomers, across both trimers. P1 and P6 form platforms that support RNA cleavage by P3. (B) Close-up of the active site (P3). Critical residues are shown in stick format. Uridine flips out to interact with S294 and N278, which provides optimal positioning for the catalytic triad. The 3′ base is stabilized by W333. (C) Cryo-EM density for the RNA engaged in the active site. (D) Time-course cleavage reaction for the dsRNA as well as each strand alone. Nsp15 cleaves ssRNA more quickly than dsRNA, and prefers different positions depending on that context. OH: alkaline hydrolysis of dsRNA. ssRNA(for) is the Cy5 labeled strand (red); ssRNA(rev) is the FI-labeled strand (blue).
