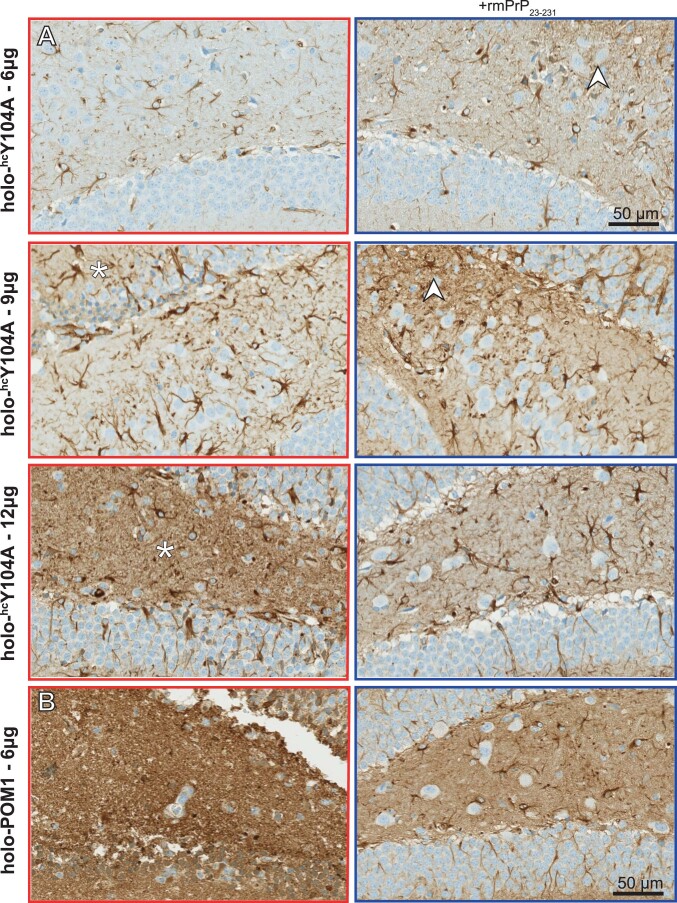
Extended Data Fig. 7. Dose-dependent gliosis of hcY104A is also conspicuous around needle tracts.
Extended Data Figure 7. (a) Photomicrographs of glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP) immunohistochemistry on consecutive sections depicted in Fig. 6c. Left column: holo-hcY104A injections (6, 9 and 12 µg). Right column: holo-hcY104A + rmPrP23–231. GFAP immunoreaction was increased in areas of neuronal damage (white asterisks) and around needle tracts (white arrowheads). (b) Micrographs demonstrating an intensive GFAP immunoreaction in areas with extensive holo-POM1 (6 µg)- induced neurotoxicity. Left panel: POM1 injection (6 µg). Right panel: holo-hcY104A + rmPrP23–231. Sections are consecutive to those shown in Fig. 6f.