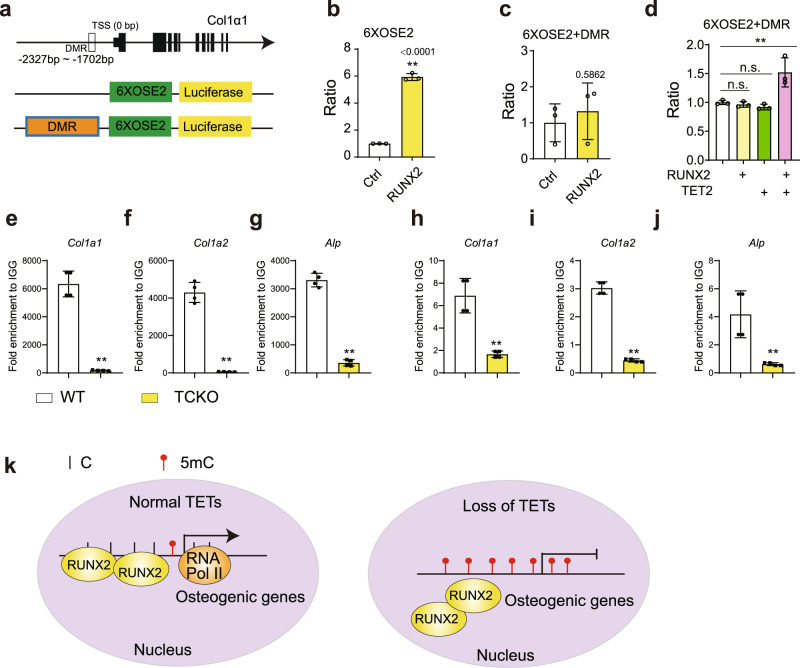
Fig. 7. RUNX2 recruits TET proteins to the promoter of target genes to facilitate transcription by modification of DNA methylation.
a The strategy for promoter luciferase assay. OSE2: Osteocalcin-specific element 2. DMR: −2327bp to −1702bp of Col1α1 promoter. b, c The measurement of luciferase activity for 6XOSE2 (b) and 6XOSE2 + DMR (c) promoter stimulated by RUNX2. **P < 0.01. Two-tailed Student’s t test. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n = 3 independent cell samples. d The measurement of luciferase activity for 6XOSE2 + DMR treated with TET2 or RUNX2 separated or combined. **P < 0.01. Ordinary one-way ANOVA. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n = 3 independent cell samples. e–g ChIP-qPCR for RUNX2 over the promoter regions of osteogenic genes including Col1α1 (e), Col1α2 (f), Alpl (g). h–j ChIP-qPCR for RNA Polymerase II (RNA Pol II) over the promoter regions of osteogenic genes including Col1α1 (h), Col1α2 (i), Alpl (j). **P < 0.01. Two-tailed Student’s t test. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n = 4 independent samples. k Based on our results, we proposed the model that RUNX2 could bind to the promoter regions of osteogenic genes. By recruiting TET proteins via RUNX2, DNA hypomethylation would be induced over those osteogenic genes and thus promote their expression by providing a more accessible chromatin landscape for transcriptional machinery such as RNA Pol II. Loss of all TET proteins would result in repression of osteogenic genes targeted by RUNX2, and thus lead to bone development failure.