FIGURE 2.
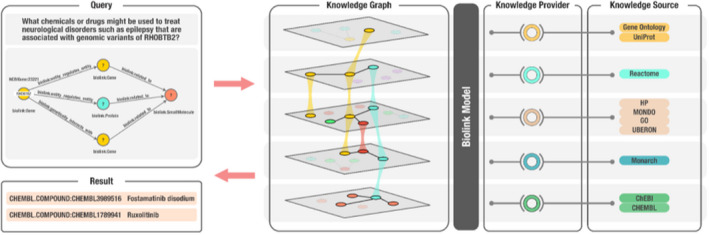
An overview of the Translator architecture that supports biomedical KG‐based question‐answering, including the role of Biolink Model, in the context of an example question. In this example, a user has posed the natural‐language question: what chemicals or drugs might be used to treat neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, that are associated with genomic variants of RHOBTB2? The question is translated into a graph query, as shown in the top left panel, which is then translated into a Translator standard machine query (not shown). The KG shown in the second panel from the left is derived from a variety of diverse “knowledge sources,” a subset of which are displayed in the figure, that are exposed by Translator “knowledge providers.” Biolink Model provides standardization and semantic harmonization across the disparate knowledge sources, thereby allowing them to be integrated into a KG capable of supporting question‐answering. In this example, Translator provided two answers or results of interest to the investigative team who posed the question, namely, fostamatinib disodium and ruxolitinib, as shown in the bottom left panel. KG, knowledge graph.
