Figure 1.
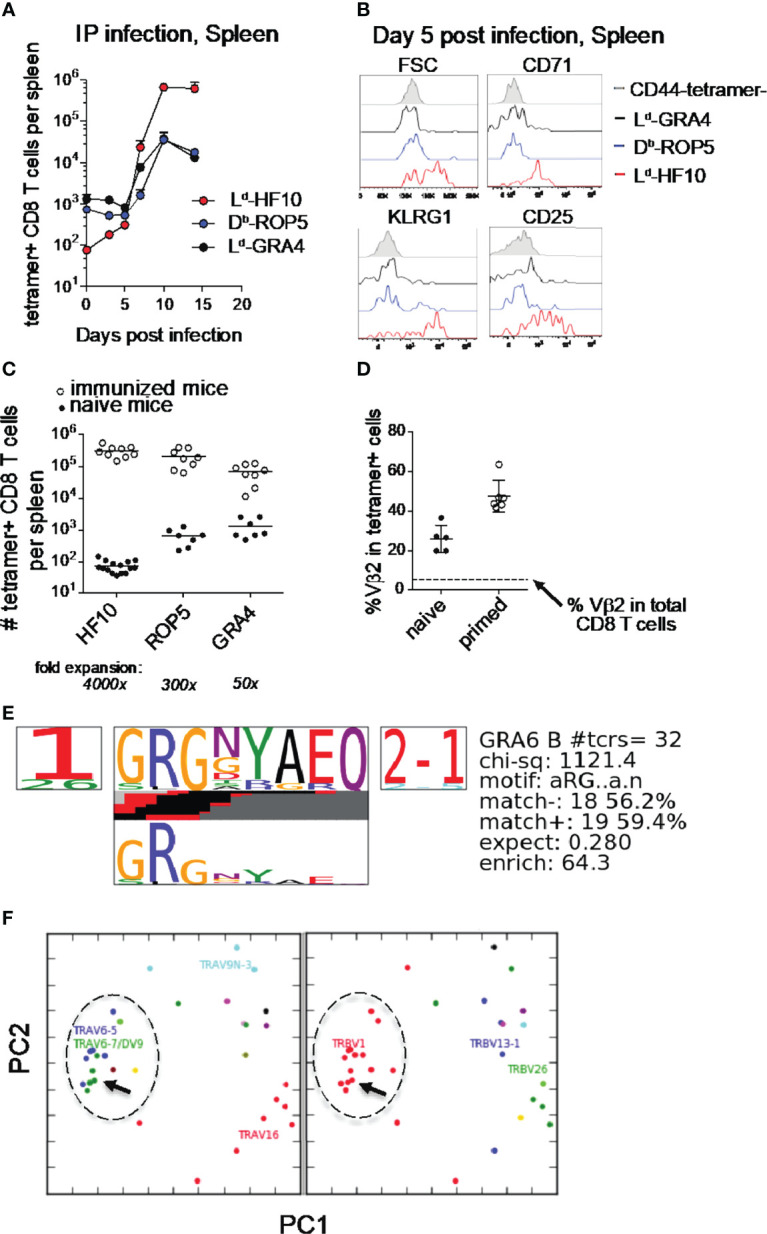
Characteristics of the Ld-HF10 specific T cell response. (A) T. gondii-specific CD8 T cells were quantified by pMHC tetramer staining and flow cytometry of splenocytes at different time points after intraperitoneal infection of F1 (B6xB6.C) mice. Fold change between naive and expanded T cells was calculated using the average number of tetramer+ cells in each population in naive mice (GRA6 = 74.4, ROP5: 654.9, GRA4: 1330). (B) Flow cytometric analysis of size (FSC or forward scatter) or expression of activation and effector markers (CD71, KLRG1, and CD25) on gated tetramer+ splenic CD8 T cells at day 5 post infection. (C) Mice were immunized with bone marrow-derived dendritic cells loaded with the indicated peptides. Expanded tetramer+ CD8 T cells were quantified by tetramer staining of splenocytes 7 days post immunization (open circles). Numbers of tetramer+ CD8 T cells in the spleen were quantified by tetramer enrichment of naïve mice and were used to calculate the fold expansion of each antigen-specific T cell population (closed circles). Statistical significance of differences in fold change between the three groups was calculated using Mann-Whitney tests. GRA6 vs. GRA4: p < 0.0001, GRA6 vs. ROP5: p < 0.0001, GRA4 vs. ROP5: p=0.0002. Statistical significance between tetramer+ T cell populations was calculated by two-way ANOVA. The interaction p-values are as follows: GRA6 vs. GRA4: p < 0.0001, GRA6 vs. ROP5: p < 0.0001, GRA4 vs. ROP5: p=0.99. (D) The frequency of Vβ2 usage amongst Ld-HF10 specific splenic CD8 T cells tetramer enriched from naïve mice or found in T. gondii-infected mice was determined by flow cytometry. Each dot represents an individual mouse and the dashed line indicates the frequency of Vβ2 amongst total splenic CD8 T cells (5.40%). (E, F) Ld-HF10 tetramer+ CD8 T cells were sorted from mice 3 weeks post infection and TCRα and TCRβ genes from individual T cells were sequenced as described (39). Clonal diversity in Ld-HF10 specific CD8 T cells was analyzed using the TCRdist algorithm (40). (E) Top-scoring CDR3β motif. Results of a CDR3 motif discovery algorithm are shown using a TCR logo that summarizes V and J usage, CDR3 amino acid enrichment, and inferred rearrangement structures. The bottom panel shows the motif enriched by calculating against a background dataset of non-epitope specific TCR sequences. (F) Principal components analysis (PCA) projection of the TCRdist landscape colored by Vα (left panel) and Vβ (right panel) gene usage. The groups of TCRs that correspond to the top scoring CDR3β motif are indicated with a dashed circle, and the TG6 TCR is indicated with an arrow.
