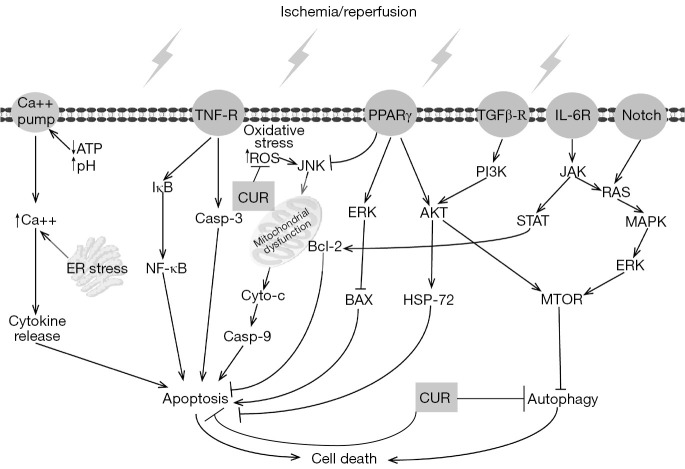
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanism demonstrating the protective function of CUR against ischemia-reperfusion injury. TNF-R, tumor necrosis factor receptor; PPAR, peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors; TGF, transforming growth factor; IL-6R, interleukin 6 receptor; CUR, curcumin; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; I-κB, inhibitor of NF-κB; Casp, caspase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; Cyto-c, cytochrome c; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; BCL2, b-cell lymphoma-2; BAX, BCL2 associated X; AKT (PKB), protein kinase B; HSP, heat shock protein; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; JAK, janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; RAS, rat sarcoma; MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; MTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin.