Fig. 3.
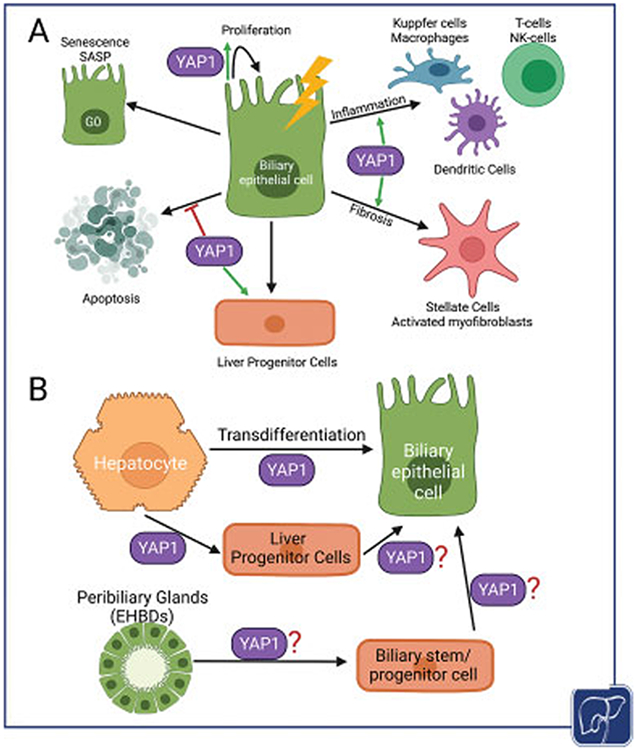
Diverse roles of YAP1 in regulating cholangiocyte and hepatocyte responses to cholestatic injury. (A) YAP1 can induce proliferation as well as promote survival of cholangiocytes during injury. Its role in activating liver progenitor compartment is also recognized. Under certain chronic and uncontrolled injury, YAP1 activation in bile duct cells could lead to ductular reaction to induce pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrogenic gene expression and in turn promote disease progression. Likewise, YAP1 might also contribute to senescence-associated secretory phenotype in bile duct cells. (B) YAP1 is known to directly induce hepatocyte to cholangiocyte transdifferentiation in adult livers. It could also lead to dedifferentiation of a mature hepatocyte to a progenitor cell which could in turn differentiate into a cholangiocyte. The role of YAP1 in liver progenitor cells arising from either peribiliary glands in the EHBDs or hepatic stem cell populations in the canal of Hering, especially in contribution to biliary repair, remains to be elucidated.
