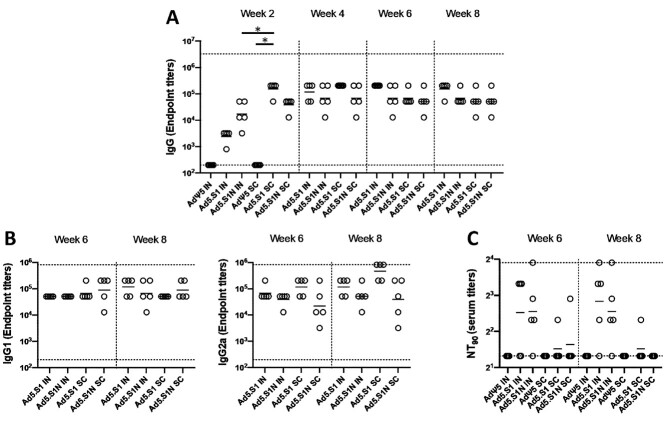
Figure 2.
Antigen-specific antibody responses in mice immunized with adenoviral-vectored SARS-CoV-2-S1N vaccine. BALB/c mice (n = 5 mice per groups) were immunized intranasally (IN) or subcutaneously (SC) with 5 × 1010 v.p. of Ad5.SARS-CoV-2-S1N (Ad5.S1N), Ad5.SARS-CoV-2-S1 (Ad5.S1), or empty Ad5 vector as negative control (AdΨ5). On weeks 2, 4, 6, and 8 after vaccination, the sera from mice were collected, serially diluted (200×), and tested for the presence of SARS-CoV-2-S1-specific (A) IgG and (B) IgG1 & IgG2 antibody levels at the indicated time points by ELISA. (C) Serum from immunized mice was tested neutralizing antibodies using a plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT) SARS-CoV-2 strain from Wuhan. Serum titers that resulted in a 90% reduction in SARS-CoV-2 viral plaques (NT90) compared to the virus control are reported at 6 and 8 weeks after immunization, respectively, and bars represent geometric means. No neutralizing antibodies were detected in serum AdΨ5 control group. Significance was determined by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons (*p < 0.05). Horizontal solid lines represent geometric mean antibody titers. Horizontal dotted lines represent minimum and maximum dilutions. Results are from a single animal experiment. (N = 5 mice per group). ELISA experiments were conducted twice while neutralizing antibody experiments were conducted once.