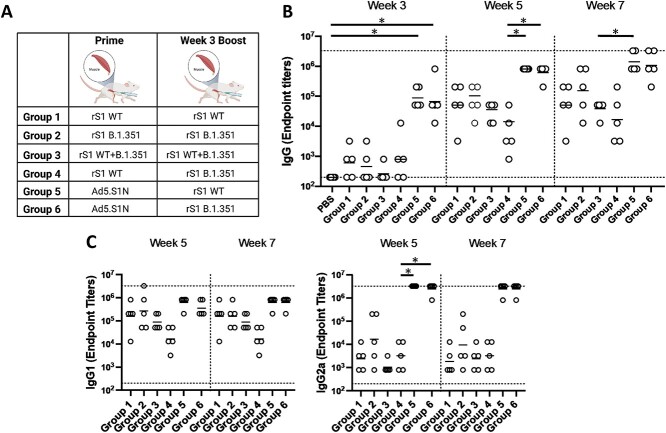
Figure 6.
Homologous and heterologous intramuscular prime-boost vaccination with variant-specific recombinant S1 proteins (rS1) and Ad5.SARS-CoV-2-S1N (Ad5.SIN). BALB/c mice (n = 5 mice per groups) were immunized and boosted intramuscularly with 45 μg of Wuhan rS1 (rS1 WT), South Africa rS1 (rS1 B.1.351), mixture of Wuhan rS1 and South Africa rS1 (rS1 WT+B.1351), or 1 × 1010 v.p. of Ad5.SARS-CoV-2-S1N (Ad5.S1N), while mice were immunized intramuscularly with PBS as a negative control. (A) Schematic layout of mice (N = 5 mice per group) vaccinations. Group 1 prime and homologous boost 15 μg rS1 WT. Group 2 prime and homologous boost 15 μg rS1 B.1.351. Group 3 prime and homologous boost 15 μg rS1 WT+B.1.351. Group 4 prime 15 μg rS1 WT and heterologous boost 15 μg rS1 B.1.351. Group 5 prime 1 × 1010 v.p. Ad5.S1N and heterologous boost 15 μg rS1 WT. Group 6 prime 1 × 1010 v.p. Ad5.S1N and heterologous boost 15 μg rS1 B.1.351. Antigen-specific antibody responses in mice immunized. On weeks 3,5, and 7 after vaccination, the sera from mice were collected, serially diluted (200×), and tested for the presence of SARS-CoV-2-S1-specific (B) IgG and (C) IgG1 and IgG2a antibody levels at the indicated time points by ELISA. Significance was determined by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons (*p < 0.05). Horizontal lines represent geometric mean antibody titers. Horizontal dotted lines represent minimum and maximum dilutions. Results are from a single animal experiment. (N = 5 mice per group). ELISA experiments were conducted twice while neutralizing antibody experiments were conducted once.