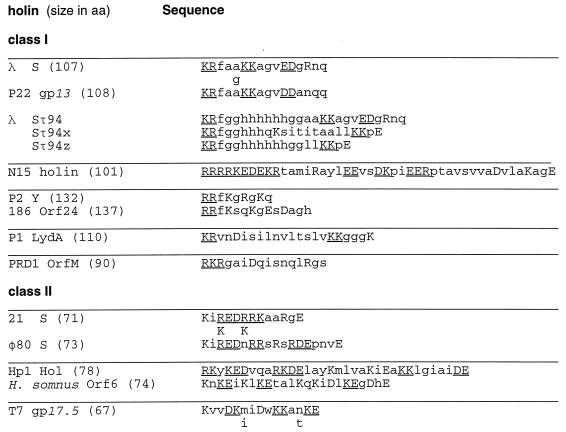
FIG. 2.
The C-terminal hydrophilic domain of holin proteins from bacteriophages of gram-negative bacteria. The C-terminal sequence of the first member identified from each of the orthologous groups of holins is shown. Holin sequences are grouped into class I (three potential transmembrane domains) and class II (two potential transmembrane domains). Each holin is given with the total number of residues for the longest form of the predicted protein product. Class I orthologous groups: λ S (four orthologs, including P22 gp13), N15 (no orthologs), P2 Y (one ortholog, 186 Orf24), P1 LydA (no orthologs), and PRD1 OrfM (no orthologs). Class II orthologous groups: 21 S (six orthologs, including φ80 S); Hp1 Orf78 (one ortholog, Haemophilus somnus cryptic holin), T7 gp17.5 1 ortholog, and T3 Lys. If an ortholog has two or fewer residues changed, the changes are shown below the representative sequence. More-divergent termini within the orthologous group are shown in their entirety. Acidic and basic residues are shown in capital letters, and two or more consecutive charged residues are underlined. The H. somnus sequence comes from a cryptic prophage (29). A compilation of holin sequences can be found in Bläsi and Young (42) and in Young (41). The phage N15 holin sequence was obtained from R. Hendrix (19). Also shown are the C-terminal sequences of the predicted products of modified S alleles where a nucleotide sequence coding for an oligohistidine tag was inserted correctly (Sτ94) and incorrectly (Sτ94x, Sτ94z) after codon 94 (35).