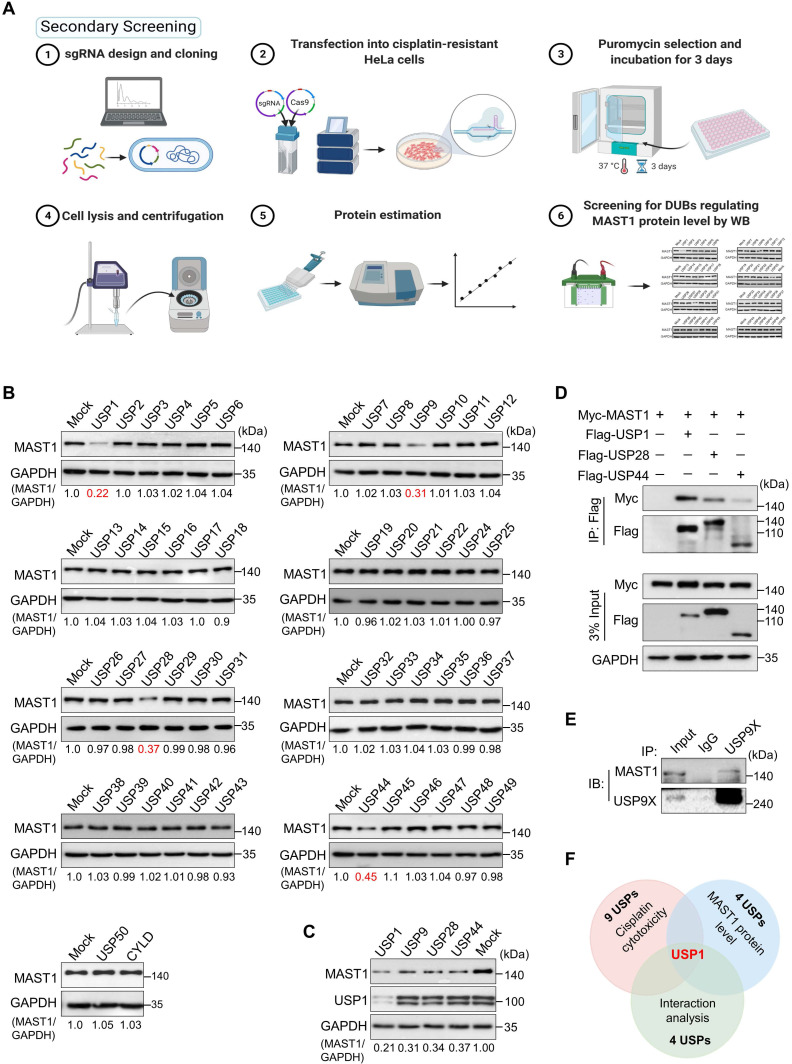
Figure 2.
DUB knockout library kit-based screening for USPs regulating MAST1 protein level by Western blot analysis. (A) Schematic representation of secondary screening with a CRISPR/Cas9-based sgRNA library to find DUBs that regulate MAST1 protein level. Steps 1-2: The designed DUB knockout sgRNA library, which consists of an entire set of genes encoding USPs, was co-transfected with Cas9 into HeLa-cisR cells (day 1). Step 3: The cells were placed under puromycin selection (2 µg/mL) and incubated for 3 days (days 2-5). Step 4: The transfected cells were harvested and lysed, and protein was isolated. Steps 5-6: Protein concentration was estimated by Bradford reagent, and equal concentrations of all DUBKO cell lysates were loaded on SDS-PAGE and screened for DUB candidates regulating endogenous expression pattern of MAST1 using Western blot (WB) analysis. (B) Equal protein concentrations from the cell lysates from (A) were subjected to Western blotting to determine the endogenous MAST1 protein level. For each blot, HeLa-cisR cells co-transfected with scrambled sgRNA and Cas9 served as the mock control. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The protein band intensities were estimated using ImageJ software with reference to the GAPDH control for each individual sgRNA (MAST1/GAPDH) and presented below the blot. (C) The effects of the targeting the putative DUB candidates on the MAST1 protein level were estimated by Western blotting. The protein band intensities were estimated using ImageJ software with reference to the GAPDH control band for each individual sgRNA (MAST1/GAPDH) ) and presented below the blot. (D) The interactions between putative DUB candidates and MAST1 by co-immunoprecipitation analysis. Myc-MAST1 and DUBs (Flag-USP1, Flag-USP28, and Flag-USP44) were transfected into HEK293 cells. (E) The interaction between endogenous USP9X and MAST1 by co-immunoprecipitation analysis. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (F) A Venn diagram showing the overlapping DUB candidate based on cisplatin cytotoxicity, loss-of-function effect on MAST1 protein level, and interaction analysis with MAST1.