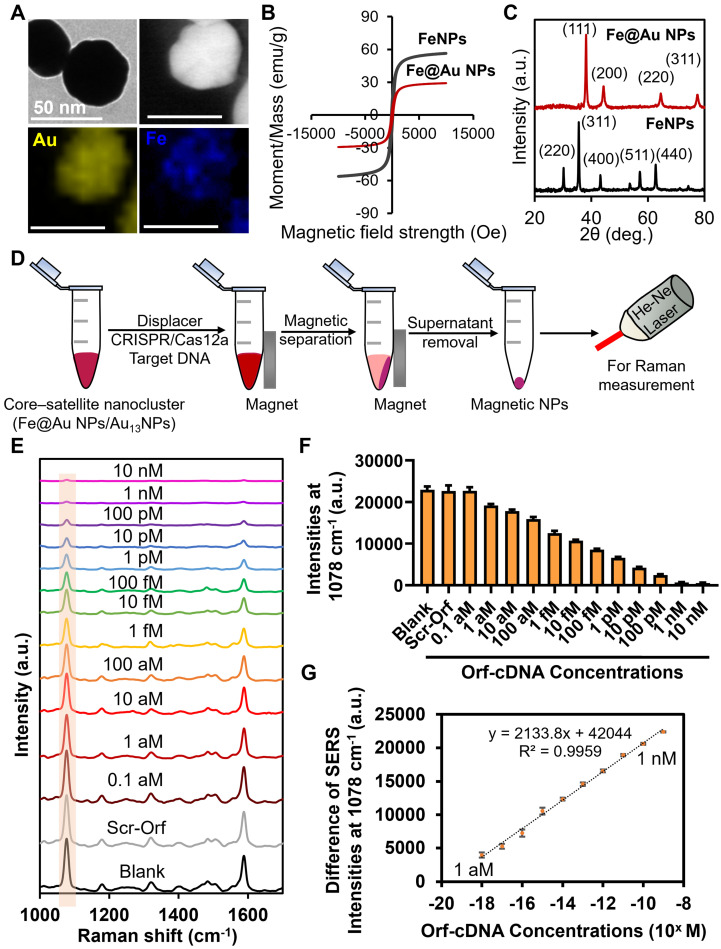
Figure 4.
Sensitivity study of detecting Orf-cDNA using the magnetic-responsive biosensing platform. (A) Representative TEM image, scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) image, and EDX elemental map of Fe@Au40 NPs. (B) By vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM) measurement, the magnetic moment per unit mass of FeNPs and Fe@Au40 NPs exhibited minimal hysteresis, and their saturation moments (Msat) were estimated to be 56 emu/g and 29 emu/g, respectively. (C) Typical XRD patterns of FeNPs and Fe@Au40 NPs, respectively. (D) Schematic illustration of magnetic reduction of background signal after detection of target DNA. Dissociated MBA/DNA2-Au13NPs without magnetic property were removed after the magnetic separation. (E) SERS spectra of the biosensing platform after detection of blank samples, Scr-Orf (1 nM), and Orf-cDNA at varying concentrations (from 0.1 aM to 10 nM), displayed from bottom to top. (F) MBA-peak intensities of the biosensing platform after detecting samples, corresponding to (E). (G) Linear relationship of the decrease of MBA-peak intensities and the log concentrations of Orf-cDNA from 1 aM to 1 nM. Error bar denotes the standard deviation resulting from three independent experiments.