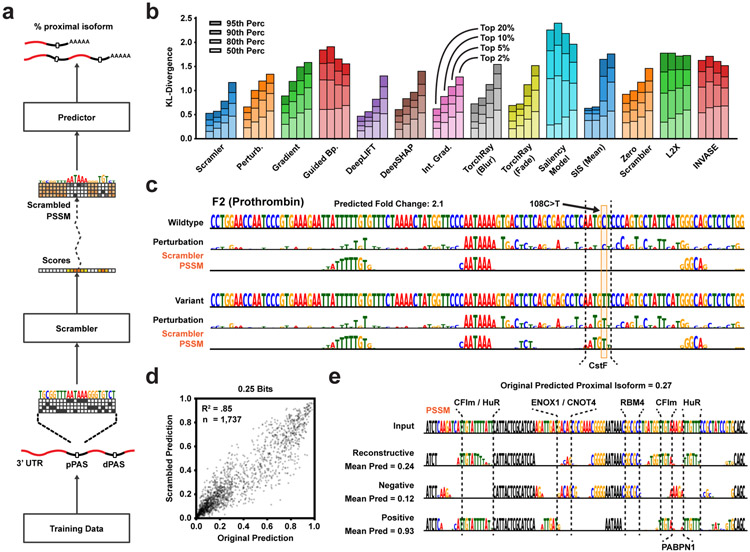
Figure 3:
APA Feature Attribution (a) Scrambler architecture for APA isoform attribution using the pre-trained model APARENT as the predictor. (b) Perturbing sequences by keeping the top X% nucleotides according to importance scores and replacing all other positions with random letters. The bar chart measures KL-divergence of APARENT-predictions between original- and perturbed test sequences (n = 1, 737). (c) Example attributions of a deleterious variant (108C>T) in the 3’ UTR of the Prothrombin (F2) gene, comparing the Perturbation method to an Inclusion-Scrambler trained on the APARENT data. (d) APARENT predictions of original test set sequences compared to predictions made on sequence samples produced by the Scrambler PSSMs. (e) Example of Inclusion-Scramblers trained to reconstruct, maximise or minimize predictions, thus finding overall important, enhancing, or repressing motifs, respectively.