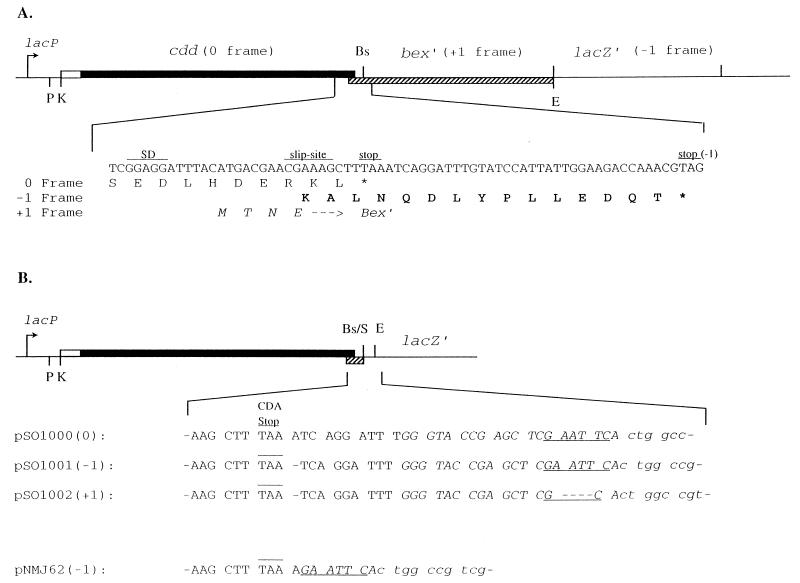
FIG. 1.
Structures of the plasmids used in this study. (A) pSO143. Thin lines, pUC19 DNA; solid bar, coding region of the B. subtilis cdd gene; open bar, leader region of the cdd gene; hatched bar, coding region of the 5′ end of the B. subtilis bex gene. Restriction endonuclease sites: E, EcoRI; Bs, BsaBI; K, KpnI; P, PstI; S, SmaI. The nucleotide sequence in the frameshift region near the end of the cdd gene, as well as the deduced amino acids encoded by the three reading frames, are shown below the graph. Capital letters, C-terminal amino acids of the wild-type CDA subunit; bold capital letters, C-terminal amino acids of the extended subunit (Sext); italicized capital letters, N-terminal amino acids of the Bex protein. (B) Nucleotide sequence of the region between the CDA stop codon and lacZ′ in various plasmids. The CDA stop codon is overlined, and the EcoRI site is underlined. pUC19 sequences are in italics, and lacZ′ sequences are in lowercase letters. Numbers in parentheses refer to the reading frame of lacZ′ relative to cdd.