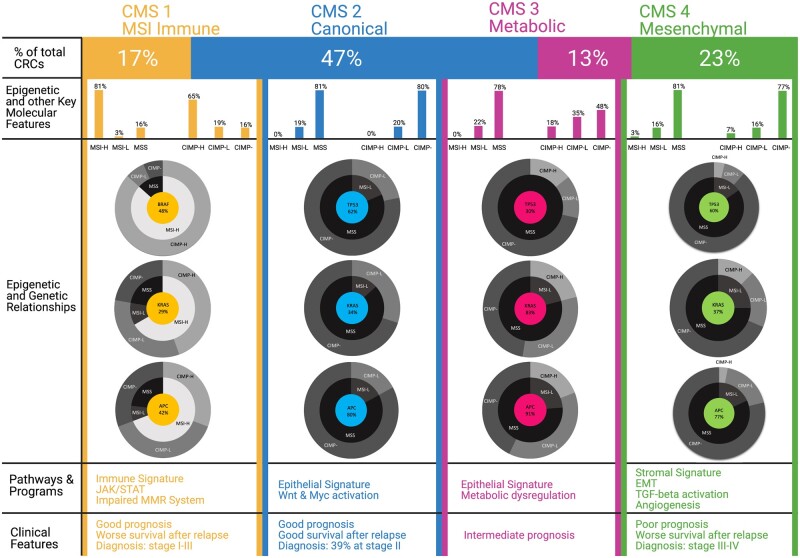
Figure 1.
Epigenetic features of the various CRC CMS subtypes. Mutation frequencies of key genes (APC, KRAS, BRAF, TP53) and the MSI status and CIMP status of CRC samples in the TCGA dataset (185 samples) available on cBioPortal is related to the consensus molecular subtypes (CMS). Each transcriptional subtype shows distinct molecular and clinical features within the CMS classification. CMS1 (MSI immune) cancers show a high MSI and CIMP status, BRAF mutations, diffuse immune infiltration, and good prognosis but worse survival after relapse. On the other hand, CMS2–4 cancers show an MSS and CIMP-low/negative status. CMS2 (canonical) cancers display a high level of CIN, loss of APC and TP53 mutations, and activation of the Wnt and MYC signaling pathways. CMS3 (metabolic) cancers are characterized by their low level of CIN, overrepresentation of KRAS mutations, and dysregulation of metabolic pathways, including carbohydrate and fatty acid oxidation. Similar to CMS2, CMS4 (mesenchymal) cancers display a high level of CIN, loss of APC and TP53 mutations, and diffuse stromal infiltration along with worse survival overall and after relapse. Figure generated using BioRender. MSI, microsatellite instability; MSS, microsatellite stable; CIMP, CpG-island methylator phenotype; CIN, chromosomal instability; MMR, mismatch repair; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.