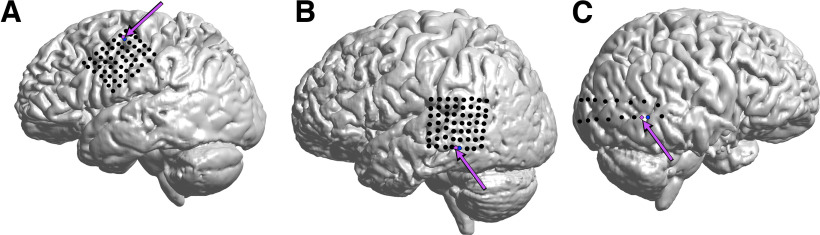
Figure 1.
ECoG Grids and microelectrode arrays. A–C, Each subject had a subdural ECoG grid placed in the frontocentral (A; subject A), middle temporal (B; subject B), or posterior temporal cortex (C; subject C), respectively. Each subject was also implanted with an MEA (magenta arrows) that allowed recording of deep cortical FP and action potentials from single neurons. The location of the ECoG channel closet to the MEA (blue) was treated as the spatial origin for computing distances across the grid.