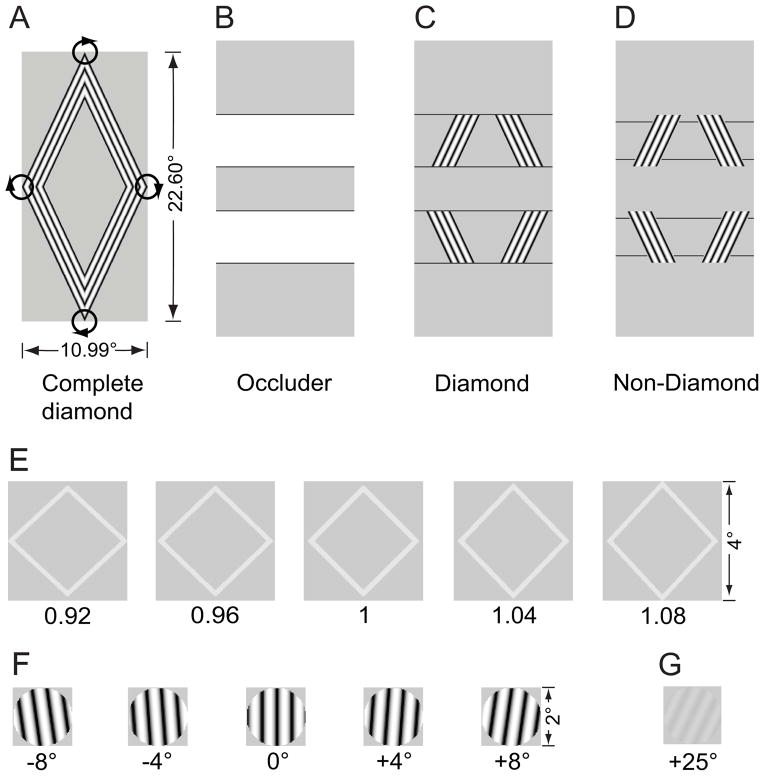
Figure 1.
Visual stimuli. (A) A complete thin diamond translated with a circular trajectory. Its direction (clockwise or counter-clockwise) reversed every 5 sec. (B) Three horizontal occluders were rendered with the background color except part of their borders – the four horizontal lines. (C) The diamond stimulus as adaptor was generated by masking the complete diamond with the occluders. T-junctions formed by the horizontal lines and the visible parts of the complete diamond made subjects see a coherently translating diamond. (D) The non-diamond stimulus as a second adaptor was generated by displacing the horizontal lines vertically. The absence of the T-junctions broke the stimulus into four separate moving bars. (E) Diamond test stimuli for measuring shape aftereffect. (F) High-contrast grating test stimuli for measuring tilt aftereffect. (G) A sample low-contrast grating test stimulus for measuring threshold elevation aftereffect.