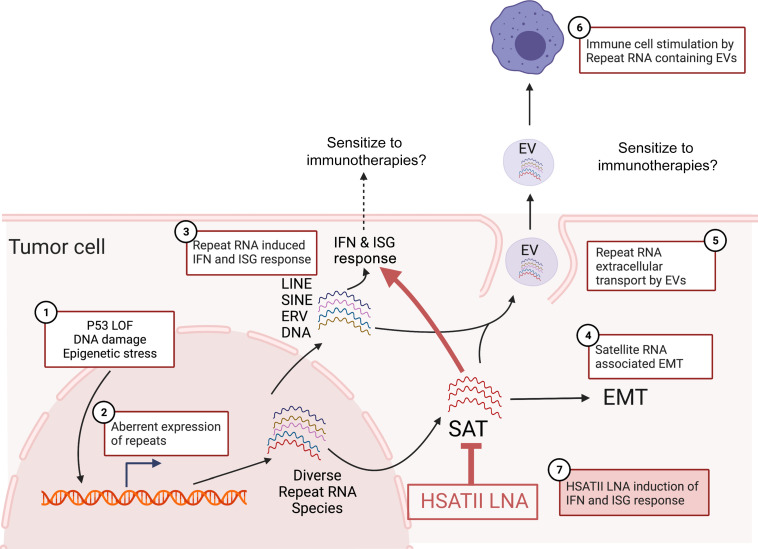
Figure 8. Working model of potential biologic and therapeutic implications of SAT RNA expression in epithelial tumor cells.
Working model depicting the reported and hypothesized tumor cell autonomous and tumor microenvironmental effects of aberrant SAT RNA expression. Various genetic and/or epigenetic alterations (1) can lead to aberrant expression of repeat RNAs (2) in cancer cells. Certain subclasses of repeat RNAs can trigger an IFN response (3) and may sensitize tumors to immunotherapies. Other repeat species, like SAT, can preferentially stimulate EMT (4). Repeat RNAs can also leave the cell in exosomes (5) and thereby stimulate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment (6), which may also sensitize to immunotherapies. These pathways can be modulated by applying LNA to specifically target SAT RNA species like HSATII (7). This model highlights the potential utility of SAT repeat RNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in EOC. LOF, loss of function.