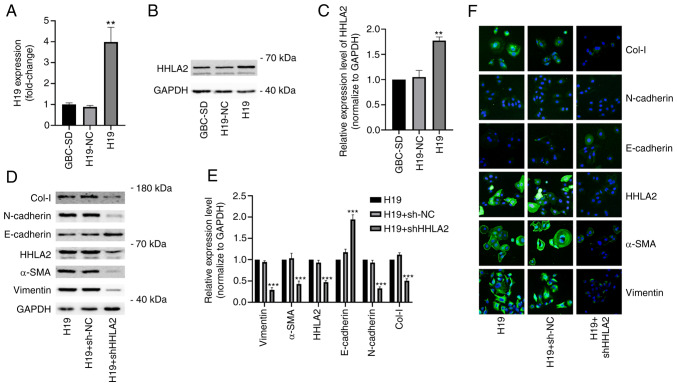
Figure 7.
Knockdown of HHLA2 inhibits H19 overexpression-induced EMT in GBC in vitro. (A) Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was used to examine the overexpression efficiency of H19. (B) Western blot analysis showed that H19 overexpression increased HHLA2 expression, (C) according to the quantification. (D) After the knockdown of HHLA2 in GBC cells stably overexpressing H19, the knockdown efficiency of HHLA2 and EMT marker expression were examined using western blotting, (E) which were quantified. Expression of EMT markers Col-I, N-cadherin, α-SMA and vimentin were decreased whilst that of E-cadherin was increased in the HHLA2 knockdown group. (n=3). (F) Similar results were observed according to the immunofluorescence staining images. Scale bars, 100 µm. Green, target protein; Blue, DAPI. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 (H19 + shHHLA2 group vs. H19 + sh-NC group). HHLA2, human endogenous retrovirus-H long terminal repeat-associating protein 2; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; GBC, gall bladder cancer; Col-I, collagen I; α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; shRNA or sh, short hairpin RNA; NC, negative control.