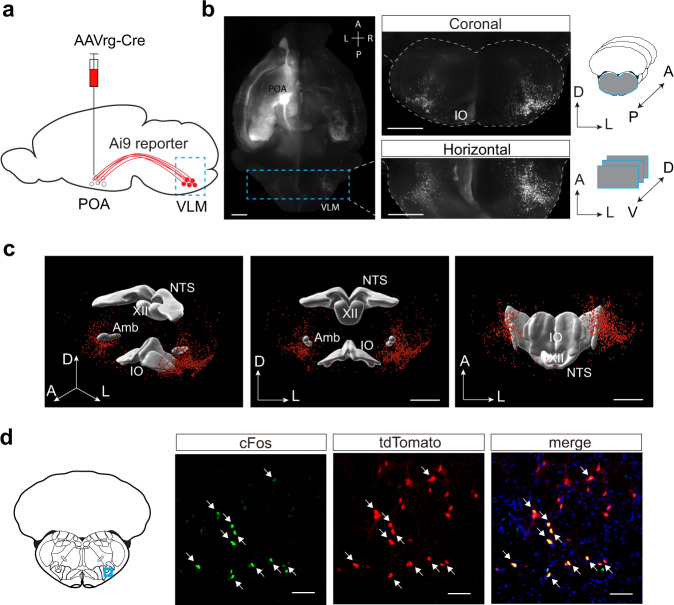
Fig. 3. Medulla glutamatergic neurons project to the preoptic area.
a Schematic illustrating retrograde labeling experiments in Ai9 reporter mice injected with AAVrg-hSyn.Cre.WPRE.hGH in the preoptic area (POA). VLM, ventrolateral medulla. b Left, maximum-intensity z stack of POA-projecting neurons in the whole mouse brain, cleared with CUBIC and imaged with light-sheet fluorescent microscopy (a representative example from 3 mice). The dashed-line box illustrating the anterior and posterior boundaries used for reconstruction of coronal and horizontal views on the right. Right top, Maximum-intensity z stack of POA-projecting neurons in the optically sliced coronal sections of the brainstem. Right bottom, Maximum-intensity z stack of POA-projecting neurons in the optically sliced horizontal sections of the brainstem. Mouse brain figures in b and d adapted from Allen mouse brain atlas. Scale bars, 1 mm. A, anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral; L, lateral. c Three-dimensional reconstruction of POA-projecting medulla neurons in the perspective, front, and ventral view, respectively (from Bregma −6.0 mm to −8.0 mm). Scale bars, 1 mm. d Fluorescence images of cFos immunostaining (green) and tdTomato expression (red) in the VLM (blue box on the coronal section) of a sleep-deprived Ai9 mouse injected with AAVrg-Cre in the POA (n = 2 mice). Arrows indicated the co-stained cells of cFos and tdTomato. Blue, DAPI. Scale bars, 50 μm. NTS nucleus of the solitary tract, XII hypoglossal nucleus, Amb nucleus ambiguus, IO inferior olivary complex.