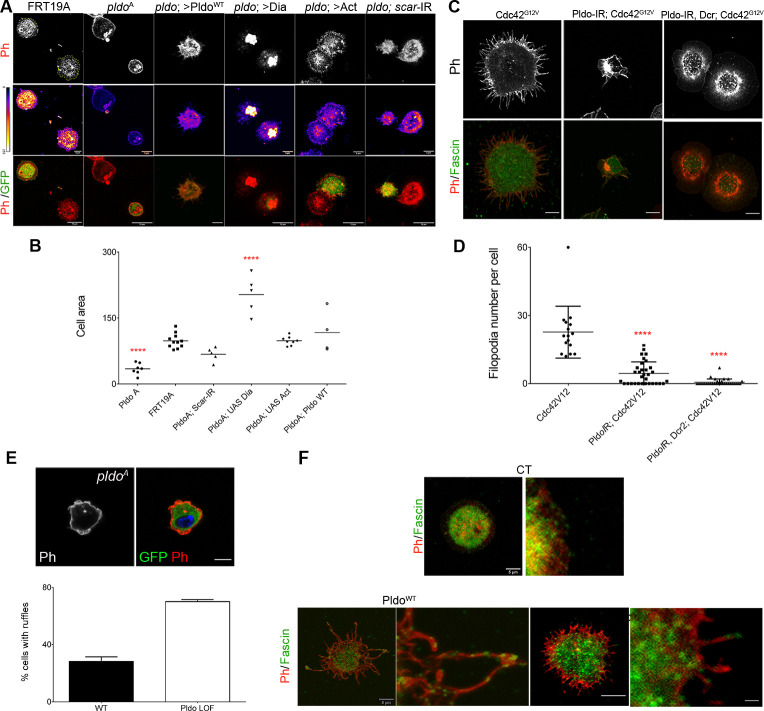
Figure S4. Pldo is essential to induce filopodia formation and to sustain cell shape in hemocytes.
(A) pldo-mutant cells were generated by the MARCM technique (expressing GFP, green cells). An FRT19A chromosome was used as a wild-type control. Note that pldo-mutant cells show a reduction in the cell attachment area that was rescued by the expression of either Pldo, Dia, or Act or by knocking down scar. Scale bars correspond to 10 μm. (B) Cell area was quantified using the phalloidin staining (red and heatmap), using at least 10 cells per genotype in each experiment (and three independent experiments). Statistical analysis was one-way ANOVA, Tukey posttest P < 0.0001. (C, D) Filopodia formation induced by the expression of Cdc42G12V in hemocytes, was evaluated by knocking down pldo. With or without Dicer expression in the LOF of Pldo, there was a significant reduction in filopodia formation by Cdc42G12V. Scale bars represents 5 μm. Number of filopodia per cell was quantified in at least 10 cells per genotype in each experiment (and three independent experiments). Statistical analysis was one-Way ANOVA, Tukey posttest P < 0.0001. (E) Ruffle formation in pldo-mutant cells. The ruffle presence was quantified in at least 10 cells per genotype in each experiment (three independent experiments). The scale bar represents 5 μm. (F) Fascin (green, staining bundled linear actin) serves as a marker for mature filopodia. Higher magnification of filopodia showing the fascin presence in the distal filopodial region in Pldo GOF or Cdc42G12V. The scale bar represents 5 and 20 μm in high magnification views.