Figure 2. Aortic Doppler in a 26‐week gestational age fetus during TdP ventricular tachycardia.
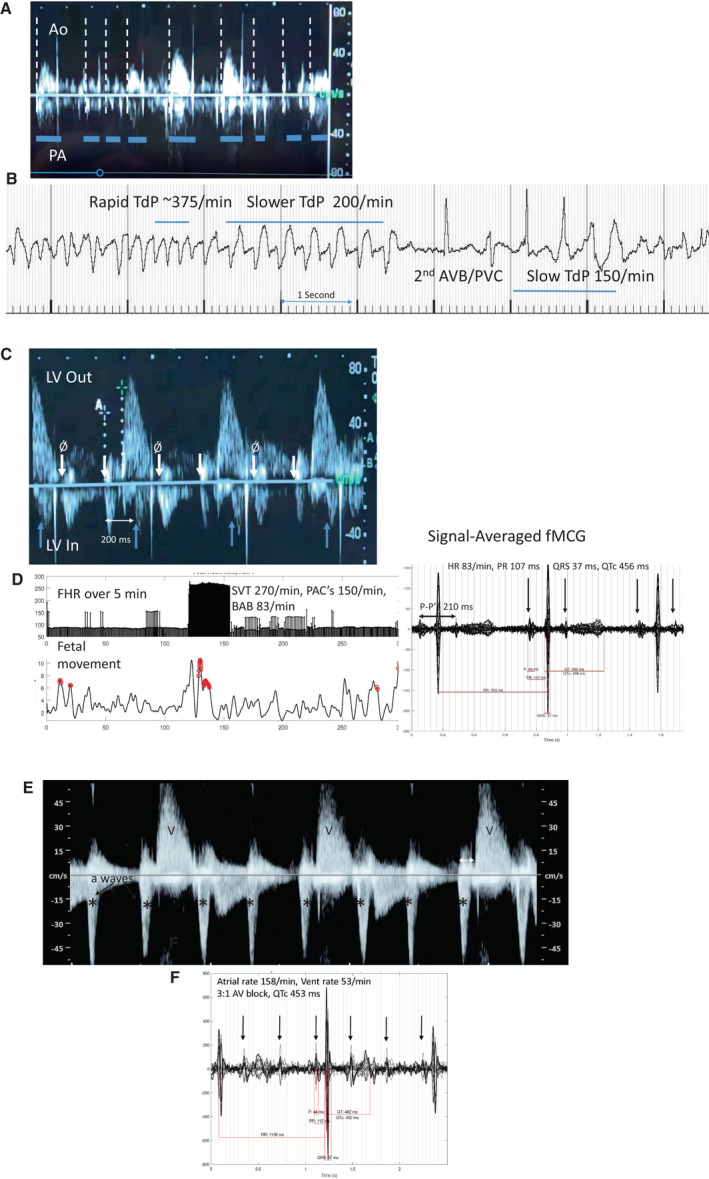
A, Doppler flow velocity onsets for pulmonary artery (downward) and aorta (upward) are not the same, suggesting bundle branch block. Hatched lines mark each systolic onset. Multiple valve clicks can be seen. Duration of systole (horizontal lines) and velocity of aortic output are also variable and attenuated in TdP, useful echo/Doppler features during evaluation, along with ventricular dysfunction. The rate of TdP is often underestimated by Doppler because of the severe and variable diminution of systolic output. B, Fetal magnetocardiography from this fetus. TdP was present 90% of the time during the recording session, alternating with 2°AVB, but because it was “normal‐rate” TdP between 150 and 200 bpm, it was not recognized as TdP by echocardiography/Doppler, and the higher rate was thought to be sinus with ectopy. C, Blocked atrial bigeminy (BAB); Doppler tracings in a 29 6/7‐week‐gestation fetus referred for suspected 2°AVB. The subject had been started on dexamethasone, but SSA antibodies were later noted to be normal. The mPR was 125 ms. Pseudo “a” waves (Ǿ arrow) were nearly equally spaced with “a” waves, suggesting 2°AV block. The real blocked ectopic velocities were discordant, because of their re‐entrant nature. During the time frame of the aortic flow velocity, but in a downward direction is the atrial “a” velocity corresponding to the p prime on fMCG (upright arrows mark onsets). These do not conduct to the ventricle, resulting in BAB with a rate of 83/min. a‐a' is ≈200 ms, closely correlating to the p–p' of 210 ms by fMCG. D, HR trend graph, actogram, and (right) 20‐s signal‐averaged tracing during BAB. Not detected by fetal echocardiography was the brief SVT episode at 270 beats/min. Stopping dexamethasone, and managing the SVT were major changes in management. E, Doppler tracing from referring hospital on a 22 3/7‐week‐gestation fetus thought to have third‐degree AV block. F, fMCG signal‐averaged tracing demonstrates a stable PR interval consistent with 3:1, 2°AVB. The subject was SSA negative. The cause of the AV block is unclear, because the QTc was normal, and postnatal genetic testing for LQTS showed no pathologic variant.*denotea atrial "A" waves. Ao indicates aortic outflow; AV, atrioventricular; AVB, atrioventricular block; FHR, fetal heart rate; fMCG, fetal magnetocardiography; LQTS, long QT syndrome; LV Out, left ventricular outflow; LV In, left ventricular inflow; mPR, mechanical PR interval; PA, pulmonary artery outflow; PACs, premature atrial contractions; PVC, premature ventricular contraction; SSA, Sjogren's antibody A; SVT, supraventricular tachycardia; TdP, torsades de pointes; and V, ventricular "V" waves by Doppler.
