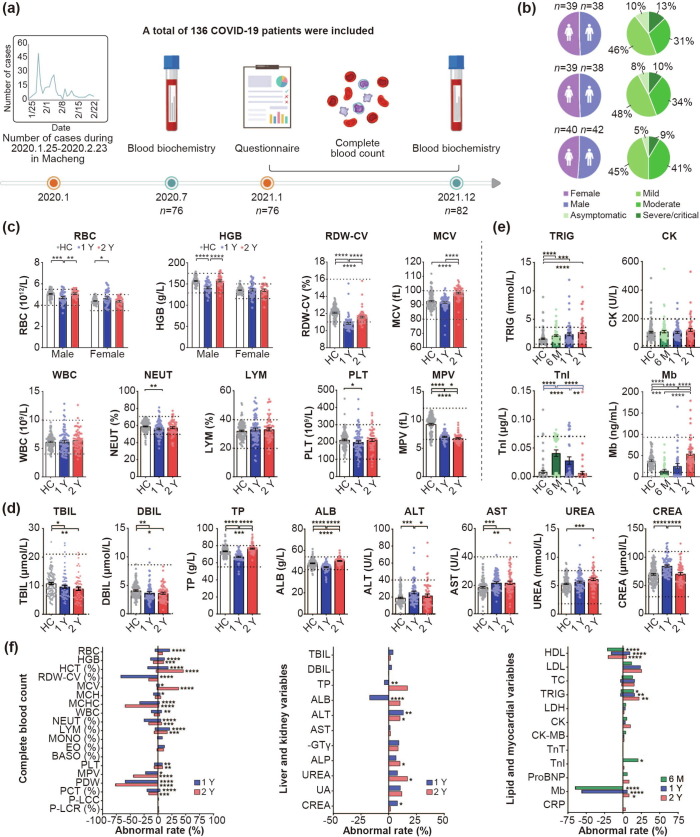
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram and blood test results of the COVID-19 convalescents during 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years follow-ups. (a) Study flow diagram. From January 25 to February 23, 2020, 253 patients with COVID-19 were confirmed in Macheng, Hubei Province, China, of whom 136 were included in the study. During the first follow-up (July 23–28, 2020), 77 participants were involved. Blood biochemical examinations about lipid and myocardial function (n = 76) were performed and some of these indicators were tested among parts of the convalescents (n = 34) because of insufficient blood samples. Until the second follow-up (January 15–16, 2021), 23 and 23 participants were lost to follow-up and were newly included (n = 77), respectively. Questionnaire and complete blood count (n = 76), and blood biochemical examinations about lipid and myocardial function (n = 63) were performed. During the third follow-up (December 21–24, 2021), 46 and 36 participants were successfully followed up and newly enrolled, respectively (n = 82). Questionnaire (n = 80) and all blood examinations (n = 59) were performed. (b) Sex composition and clinical types of participants. (c–d) Comparison of blood cell counts (c) and liver- and kidney-related variables (d) between 1- and 2-year COVID-19 convalescents and healthy controls. HC: healthy control (white, n = 125). 1 Y: About 1 year post disease onset (blue, n = 76); 2 Y: About 2 years post disease onset (red, n = 59). (e) Lipid and myocardial-related variables of 6-month, 1- and 2-year COVID-19 convalescents were compared with healthy controls. 6 M: 6-month (green, n = 76 for TRIG and CK, n = 34 for TnI and Mb due to insufficient blood sample), 1-year (blue, n = 63 for TRIG and CK, n = 34 for TnI and Mb), 2-year COVID-19 convalescents (red, n = 59) and healthy controls (white, n = 125 for TRIG and CK, n = 75 for TnI and Mb). Each point corresponds to an individual, and bar values represent the mean and standard error of the mean. The dashed lines indicate the normal reference range issued by the testing institution. Approximately >25% (28.8%, 23.2%) of healthy controls corresponding to the ALB and TRIG indicators did not meet the reference range; thus, the normal range of these indicators was set as the 5%–95% percentile range of the healthy controls. (f) The normal rate of each indicator of the convalescents. The right side of the line at 0 is the proportion higher than the reference normal values issued by the testing institution, whereas the left side means lower. The asterisk indicates a significant abnormal rate compared with the corresponding healthy controls. Mann–Whitney U test was used for (c–e) and Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test was used for (f). Two-tailed P-values were calculated. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. RBC, red blood cell; HGB, hemoglobin; RDW-CV, red-blood-cell distribution width-coefficient of variation; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; WBC, white blood cell; NEUT, neutrophil; LYM, lymphocyte; PLT, platelet; MPV, mean platelet volume; TBIL, total bilirubin; DBIL, direct bilirubin; TP, total protein; ALB, albumin; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CREA, creatinine; TRIG, triglyceride; CK, creatine kinase; TnI, troponin I; Mb, myoglobin; HCT, hematocrit; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; MONO, monocyte; EO, eosinophil; BASO, basophils; IBIL, indirect bilirubin; GLO, globulin; A/G, albumin/globulin; AST/ALT, aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase ratio; γ-GT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; UA, uric acid; HDL, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TC, total cholesterol; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CK-MB, creatine kinase isoenzyme; TnT, troponin T; ProBNP, pro-brain natriuretic peptide; CRP, C-reactive protein.