FIGURE 1.
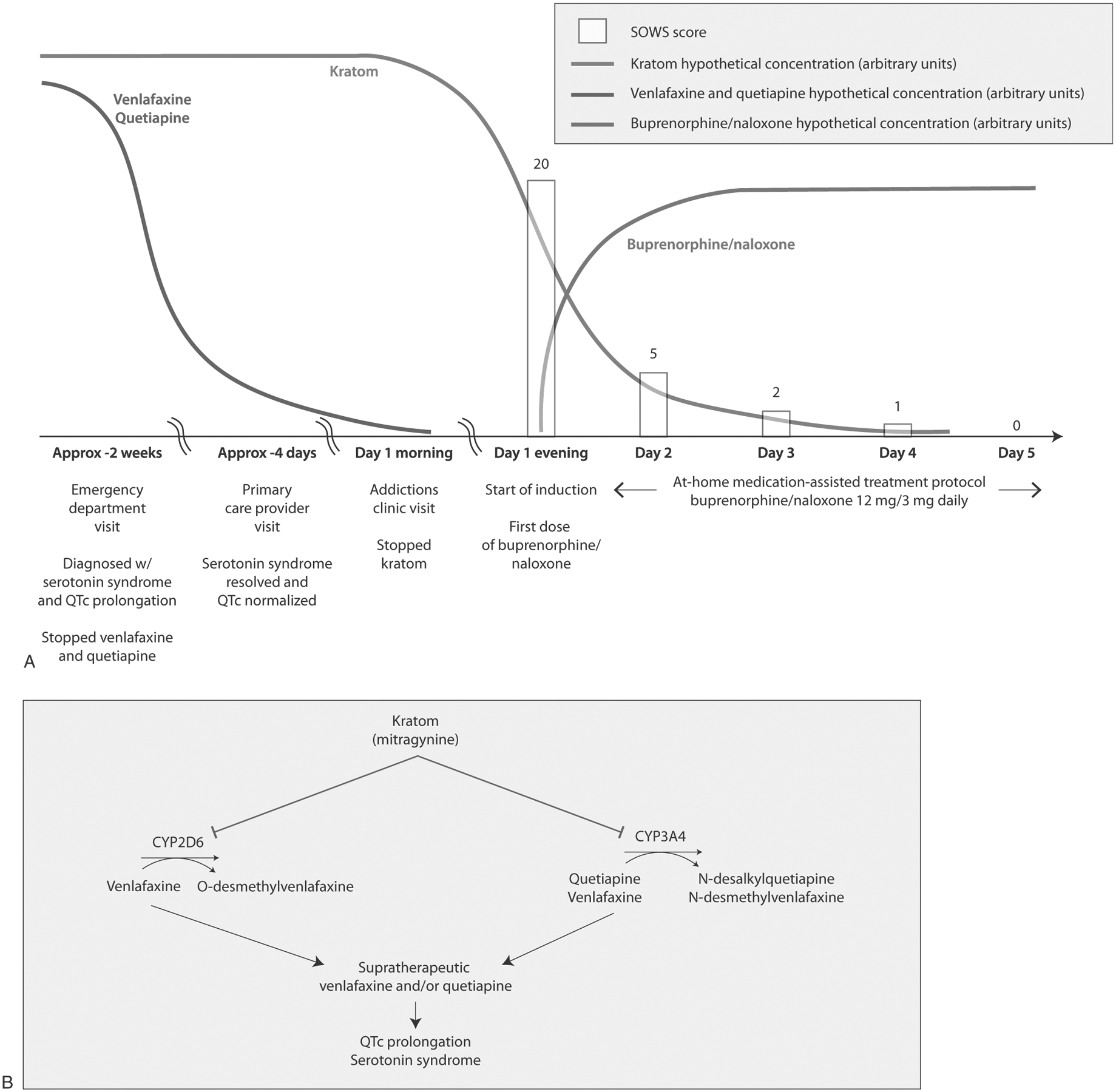
Buprenorphine/naloxone induction to support discontinuation of kratom and proposed mechanisms of pharmacokinetic kratom-drug interaction interactions. A, The timeline of this case and the buprenorphine/naloxone home induction is illustrated. A patient with kratom use disorder who consumed ~90 g kratom, 150 mg venlafaxine, and 300 mg quetiapine daily presented to the emergency department with serotonin syndrome and QTc interval prolongation. These symptoms resolved upon discontinuation of venlafaxine and quetiapine. The patient then visited a primary care provider, who referred him to an addictions clinic to assist with kratom cessation. The addictions clinic started him on a home induction with a titration to buprenorphine/naloxone 12 mg/3 mg total daily. SOWS assessments were conducted once daily, beginning with the first dose of buprenorphine/naloxone. The patient completed SOWS assessments through day 5 post home induction on buprenorphine/naloxone 12 mg/3 mg daily. B, Proposed mechanisms underlying potential interactions between the kratom alkaloid mitragynine, the CYP2D6/3A substrate venlafaxine, and the CYP3A4 substrate quetiapine. Mitragynine, typically the most abundant kratom alkaloid in kratom products, is a time-dependent inhibitor of CYP3A and a reversible inhibitor of CYP2D6.5 CYP2D6 is the major route of clearance for venlafaxine, whereas CYP3A is the major route of clearance for quetiapine and a minor route of clearance for venlafaxine.7,8,10 Quetiapine may have inhibited this minor route of venlafaxine clearance, although the resulting effect on venlafaxine concentrations is probably minor.16 Additionally, kratom alone can produce symptoms associated with serotonin syndrome and QTc interval prolongation.17
