Fig, 7. Oligomerization of GPCRs with orphan GPCRs, truncated GPCRs and RAMPs.
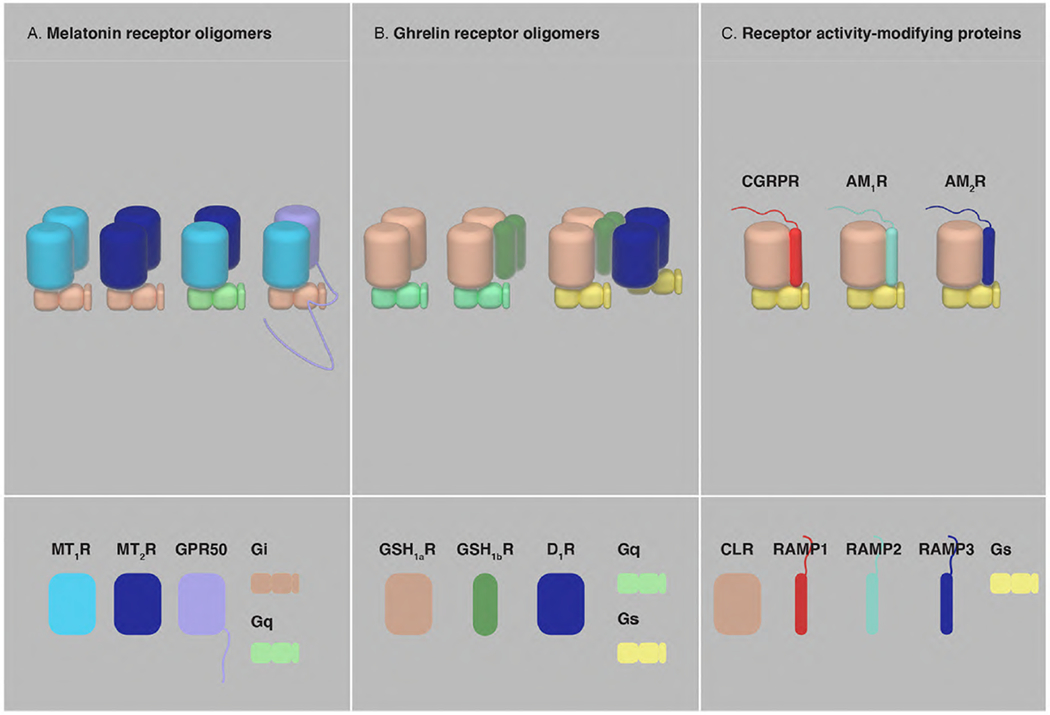
(A) Homomers and heteromers of MT1R, MT2R and GPR50. MT2R preferentially exists as a heteromeric complex with MT1R and MT1R-MT2R heteromerization drives a change in the preference of G protein subtype coupling, from Gi to Gq. The long CT of GPR50 significantly alters MT1R-Gi protein signaling in the MT1R-GPR50 heteromer (see text). (B) GHS1aR forms homomers and oligomerizes with its non-functional truncated isoform GHS1bR to form homomers and heteromers. One of the properties of the GHS1aR-GHS1bR oligomers is the facilitation of an additional interaction with the D1R, leading to a change in the preference of G protein subtype coupling of GHS1aR, from Gq to Gs. (C) The single TM domain proteins RAMP1, RAMP2 and RAMP3 associate with CLR and form the Gs protein-coupled receptors CGRP, AM1R and AM2R, respectively, determining the ligands potentially binding to CLR.
