Fig. 4.
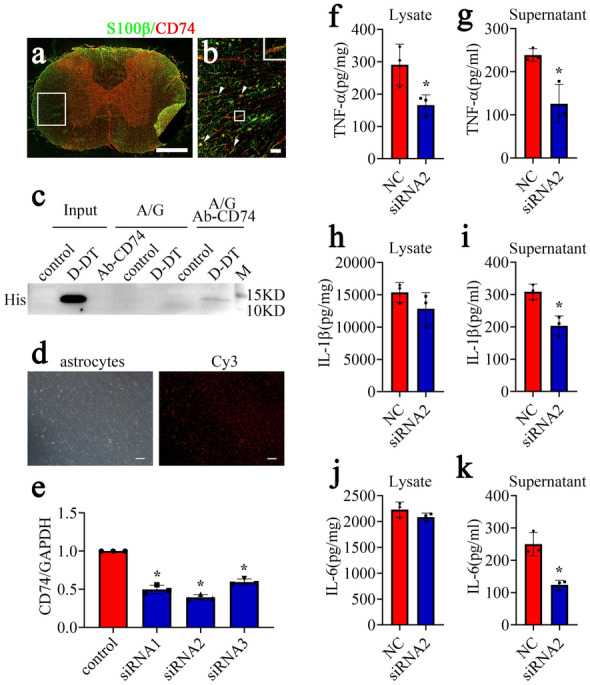
D-DT promoted astrocytic production of inflammatory cytokines through interaction with CD74 receptor. a, b Immunofluorescence showed colocalization of CD74 with S100β-positive astrocytes in the spinal cord. Rectangle indicates region magnified. Arrowheads indicate the positive signals. c Binding assay of D-DT with CD74 receptor in the primary astrocytes. The immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-CD74 antibody (Ab-CD74), followed by detection of the components of the CD74-associated complexes with anti-His antibody. The control meant that the astrocytes were stimulated with 0.01 M PBS, and the D-DT indicated that the astrocytes were stimulated with 1 µg/ml recombinant D-DT protein with N-terminal His-tag. d Determination of siRNA transfection efficiency by Cy3 control. e Interference efficiency of three siRNA oligonucleotides for CD74 was measured by RT-PCR, and siRNA2 was used for the knockdown experiments. f-k Determination of TNF-α (f, g), IL-1β (h, i) and IL-6 (j, k) by ELISA from astrocytes following CD74 knockdown for 48 h and subsequent stimulation with 1.0 µg/ml recombinant D-DT protein for 24 h. Scrambles were used as control. Scale bars, 500 μm in (a), 50 μm in (b) and (d). Experiments were performed in triplicates. Error bars represent the standard deviation (*P < 0.05)
