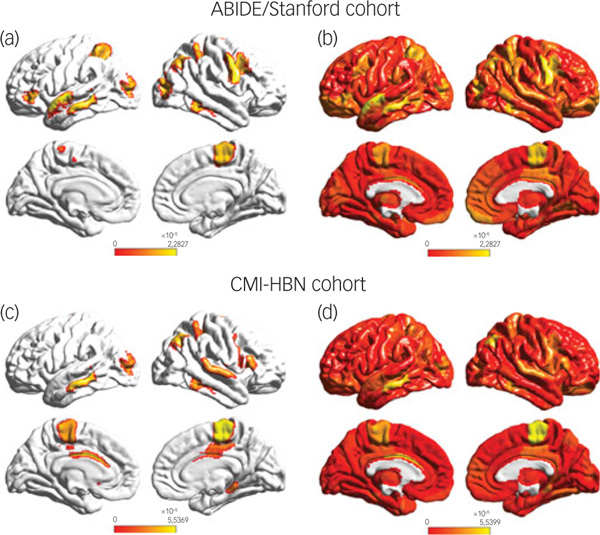
Fig. 4.
(a) Feature attribution map showing the top 5% features that underlie females with ASD versus males with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) classification in the ABIDE/Stanford cohort. Spatiotemporal deep neural network (stDNN) with integrated gradients identified brain features that distinguish females with ASD from males with ASD. The algorithm automatically identified distinguishing features in the primary motor cortex and the supplementary motor area, which anchor the motor network, middle and superior temporal gyri, which anchor the language network, as well as the visuospatial attentional system (see Supplementary Table 7 for a detailed listing of brain areas and predictive feature weights). (b) Visualisation of (unthresholded) feature weights across the whole brain in the ABIDE/Stanford cohort. (c) Feature attribution map showing the top 5% features showing replication of predictive motor network, language network, and visuospatial attention features in the Child Mind Institute-Health Brain Network (CMI-HBN) cohort (see Supplementary Table 8 for a detailed listing of brain areas and predictive feature weights). (d) Visualisation of (unthresholded) feature weights across the whole brain in the CMI-HBN cohort.