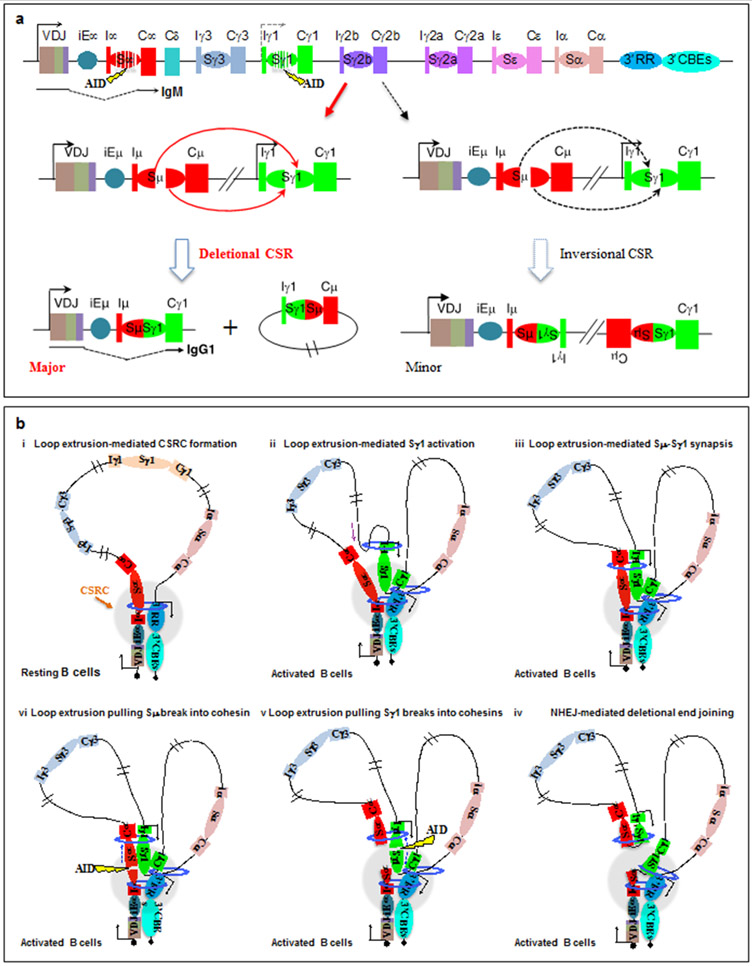
Figure 7 ∣. Loop extrusion mediates physiological, deletional class-switch recombination.
a ∣ Schematic of the 200 kb CH region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain (Igh) locus, including the V(D)J exon, the intronic Igh enhancer iEμ, the various CH exons with inducible (I) exon and promoter upstream of each CH segment, S regions, the 3′ Igh regulatory region (3′IghRR) super-enhancer and the 3′ Igh CTCF sites. AID-initiated breaks within Sμ and an activated target Sγ1 are illustrated, which can lead to deletional or inversional class-switch recombination (CSR) outcomes for Sμ to Sγ1 joining. Deletional CSR is the major physiological event, whereas inversional CSR occurs at a lower frequency. Part a is adapted with permission from REF. 13. b ∣ Loop extrusion mediates formation of a class-switch recombination-centre (CSR-centre) and promotes the synapsis of S region double-strand break ends for deletional joining. In resting B cells (part i), cohesin is loaded at 3′ IghRR or iEμ–Sμ and then extrudes the 3′IghRR and iEμ–Sμ into proximity to generate a dynamic CSR-centre. In activated B cells (part ii), a primed S–CH unit (Sγ1–Cγ1 is shown as an example) is extruded to the CSR-centre for transcriptional activation and cohesin loading, which leads to further extrusion to align acceptor and donor S regions (part iii). Tension pulls S region double-strand break ends initiated by AID into opposing cohesin rings (parts iv and v), stalling extrusion and aligning them for deletional joining mediated by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) (part vi). Part b is adapted with permission from REF. 30. See also Supplementary Video 2.