Figure 3.
Reduced COVID-19 disease markers after BCG vaccination
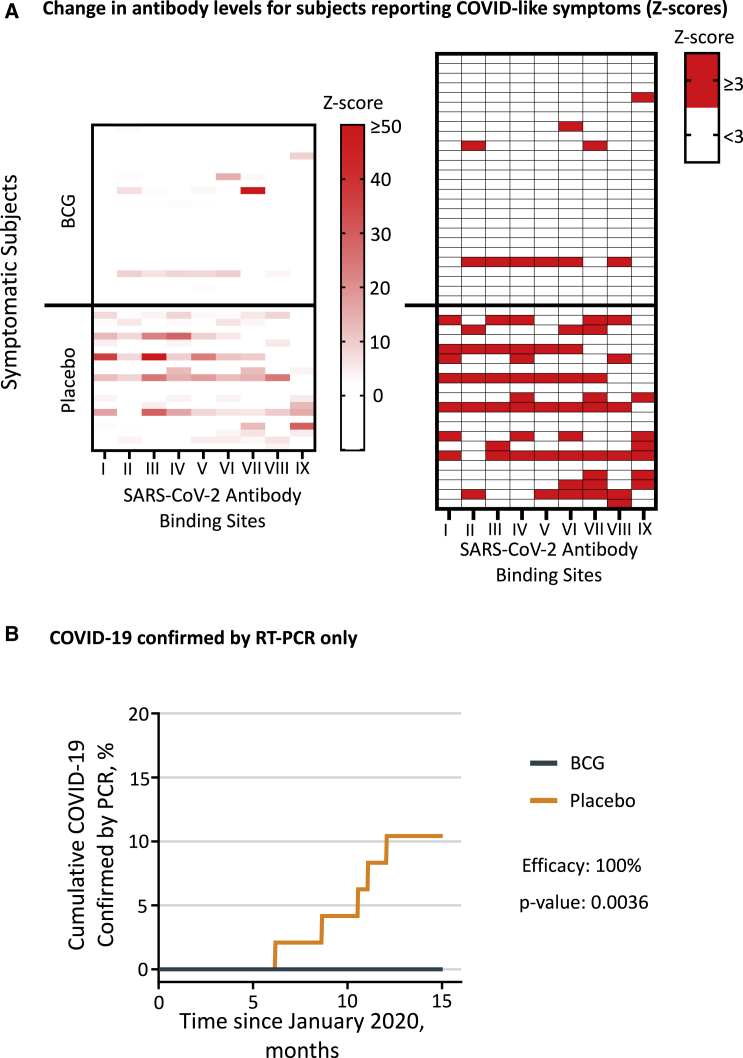
(A) The heatmaps show Z scores for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in BCG- and placebo-treated symptomatic subjects (BCG n = 26, placebo n = 21). Since some of the Z scores in the left map are faint, the right map shows which Z scores are ≥3. The Roman numerals at the bottom of each lane denote antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 protein regions as listed in Figure S1. The maximum Z score in the left heatmap was 126.
(B) Cumulative incidence of confirmed COVID-19 defined by symptomatic subjects testing positive solely by PCR. The BCG group (n = 96) had no symptomatic subjects who were PCR positive (0%), whereas the placebo group (n = 48) had 5 symptomatic and PCR-positive subjects (10.4%). This difference was significant (Fisher’s exact p = 0.0036) and translated to a vaccine efficacy of 100% with 0.99 posterior probability. There was low availability of positive PCR tests at point-of-care locations during the first 7 months of the trial. This, together with the need to perform the PCR test in a narrow window of about 2 weeks to be positive, is the reason why we designed the 9 non-PCR methods shown in Figures 2A, 2B, and 3A.