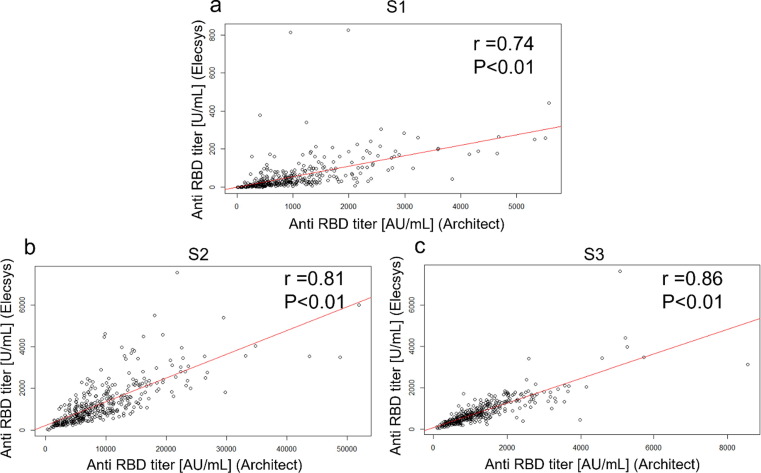
Fig. 2.
The correlation between anti-RBD antibody titers measured by the Architect assay and those measured by the Elecsys assay at each time point. (a) Scatterplot showing correlation between anti-RBD antibodies measured by the Architect assay and anti-RBD antibodies measured by the Elecsys assay at S1; (b) Scatterplot showing correlation between anti-RBD antibodies measured by the Architect assay and anti-RBD antibodies measured by the Elecsys assay at S2; (c) Scatterplot showing correlation between anti-RBD antibodies measured by the Architect assay and anti-RBD antibodies measured by the Elecsys assay at S3; anti-RBD: anti-SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain spike protein IgG; Architect: Architect SARS-CoV-2 IgG Ⅱ Quant (Abbott Laboratories); Elecsys: Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (Roche Diagnostics); S1: Within 1 week before the second vaccination, S2: 4–5 weeks after the second vaccination, and S3: 6 months after the second vaccination. The correlation between anti-RBD antibody titers measured by the Architect assay and those measured by the Elecsys was evaluated using Spearman's correlation coefficient (r). The red line indicates the regression line. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)