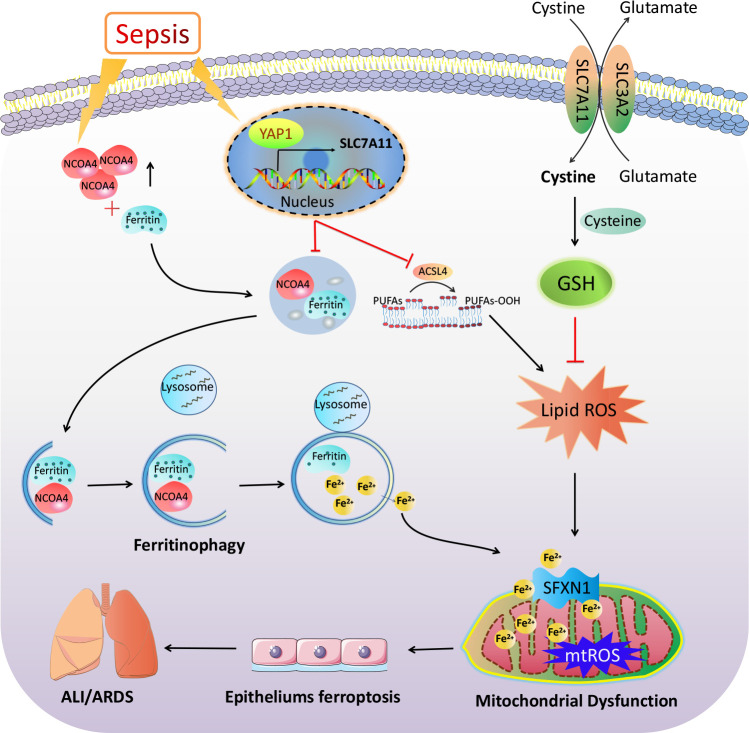
Figure 8.
The mechanism illustration on the involvement of YAP1 in ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Sepsis induces increased intracellular NCOA4 expression, which then has an interaction with ferritin and brings about the autophagic degradation of ferritin. YAP1 can suppress the degradation of ferritin into autophagosomes via inhibiting NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy, then prevent ferrous iron from transporting into the mitochondria. YAP1 attenuates the accumulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation and contributes to protecting mitochondrial function and repressing ferroptosis. Therefore, we conclude that YAP1 is involved in sepsis-induced acute lung injury by regulating the process of ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis.