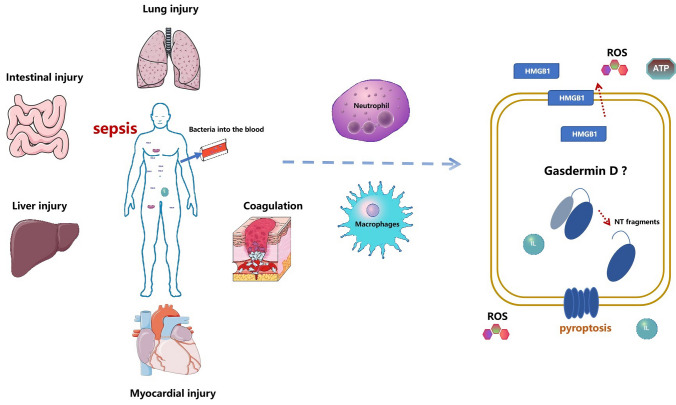
Fig. 2.
GSDMD dominates organ damage, cellular and molecular regulation in sepsis. During sepsis, bacteria enter the blood, neutrophils increase the release of pro-inflammatory factors, reactive oxygen species and HMGB1, and the body produces coagulation dysfunction, lung injury, myocardial injury, liver injury, and intestinal injury. GSDMD, which functions as a motor, is usually involved in the damage of these molecules and the body