Figure 1. Structure of the C/EBP transcription factor family.
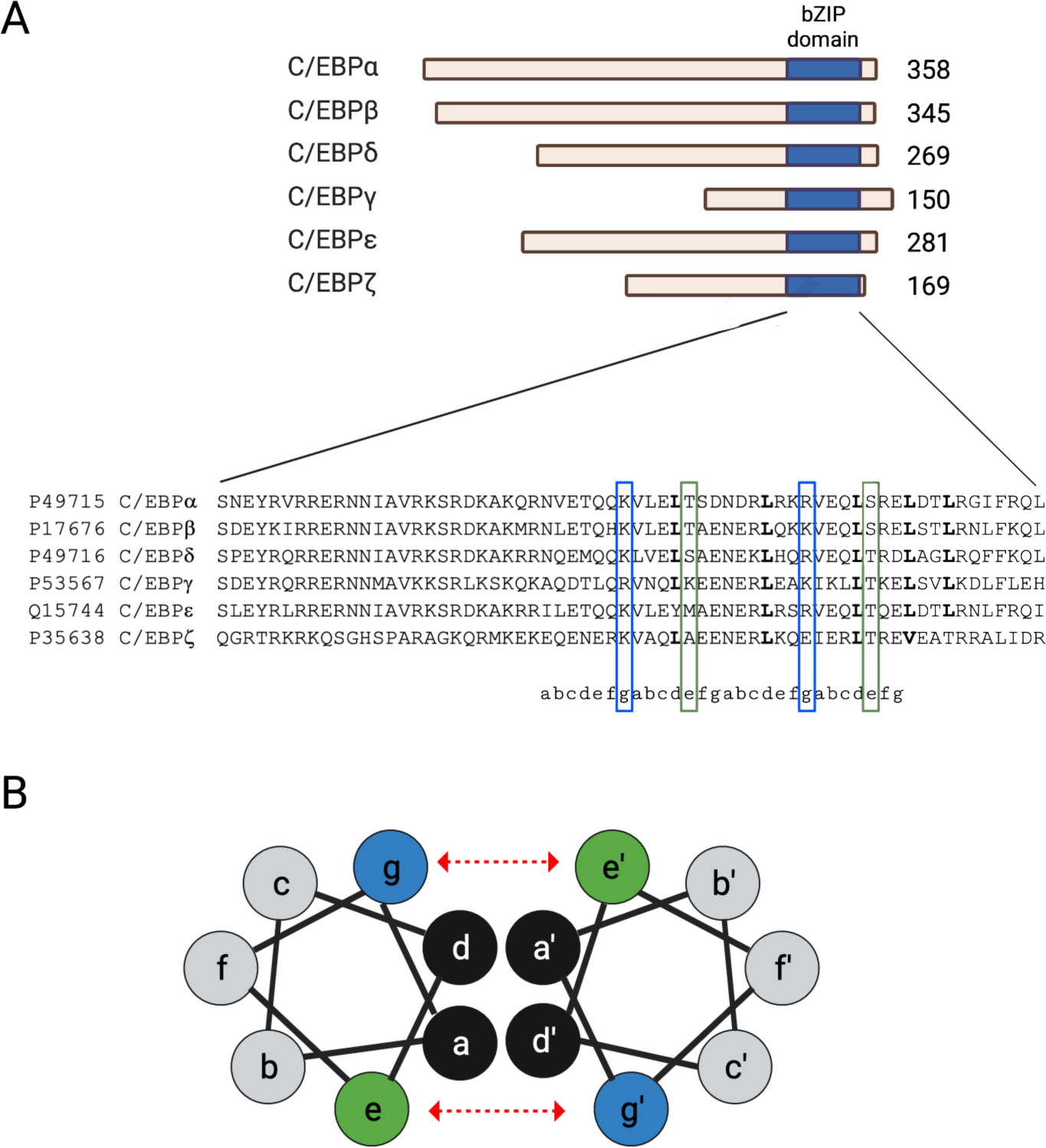
A) Scaled schematic representation of the 6 isoforms of the C/EBP transcription factor family (top). Protein sizes are provided to the right of each isoform. C/EBPγ does not contain the N-terminal activation and regulatory sequences that regulate the activity of other isoforms. The c-terminus of each isoform has a highly conserved bZIP domain (blue) which contains a basic region and a leucine zipper motif. The leucine zipper motif determines the dimerization partner for a specific C/EBP isoform. Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of bZIP the C/EBP isoforms retrieved from the Clustal Omega database (bottom). B) Cross-sectional view of the α-helix within bZIP dimer showing the amino acid positions (a through g) of the the heptad repeat of the leucine zipper. Leucine, designated by the letter “d”, interacts with other hydrophobic residues (i.e., “a”) which constitutes a low affinity interaction of the proteins (black). Electrostatic interactions between e (blue) and g (green) amino acids determine the dimerization specificity and serve to strength the interaction between C/EBP proteins (show by dashed, red arrows).
