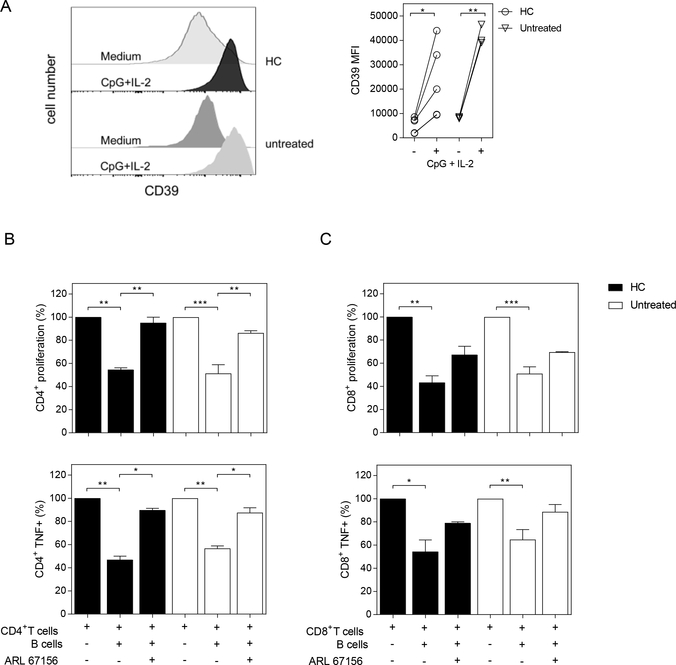
Figure 2. CD39-dependent inhibition of T cell proliferation and cytokine production by activated B cells from HC and untreated RA patients.
A) Histograms and graph show CD39 expression (determined as MFI) on purified CD19+ B cells from HC or untreated RA patients incubated with medium alone (−) or with CpG+IL-2 (+) for 72 h. B-C) Purified CD19+ B cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were obtained from PBMC of HC and untreated RA patients. CD19+ B cells were stimulated with CpG+IL-2 and then washed and incubated 2:1 with autologous CFSE-labeled CD4+ or CD8+ T cells cultured with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 mAb (plate bound) in absence or in presence of CD39 inhibitor (ARL 67156). T cell proliferation and TNF expression were analyzed by flow cytometry on CD3+CD19− live cells, after 72 h of culture. Percentage of proliferation and TNF production on (B) CD4+ T cells and (C) CD8+ T cells cultured in medium or in presence of CpG-activated CD19+ B cells with or without ARL 67156. Mean ± SEM of five independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. One-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni’s post-test were used.