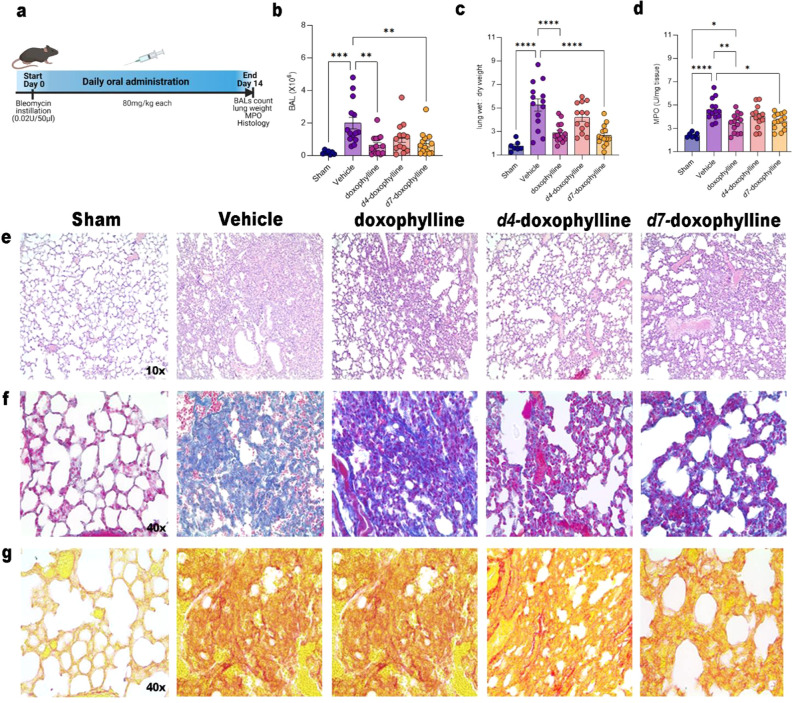
Figure 6.
Model of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin. Doxophylline and d7-doxophylline attenuate BLM-induced structural damage and lung fibrosis in mice. (a) Representative scheme of the BLM-induced lung injury model. (b) Total BAL cellularity of sham mice (not treated) and bleomycin-treated mice (treated or not with 80 mg/kg doxophylline, d4-doxophylline, or d7-doxophylline). Results are reported as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (c) Wet/dry lung weight ratio of sham and bleomycin-treated mice (treated or not with 80 mg/kg doxophylline, d4-doxophylline, or d7-doxophylline). Results are reported as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (d) MPO activity in lungs of sham and bleomycin-treated mice (treated or not with 80 mg/kg doxophylline, d4-doxophylline and d7-doxophylline). Results are reported as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (e) Representative images of H&E staining of sham and bleomycin-treated mice (treated or not with 80 mg/kg doxophylline, d4-doxophylline, or d7-doxophylline). (f, g) Representative images of (f) Masson’s trichrome staining and (g) Picrorius red staining of sham and bleomycin-treated mice (treated or not with 80 mg/kg doxophylline, d4-doxophylline, or d7-doxophylline). p values: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.