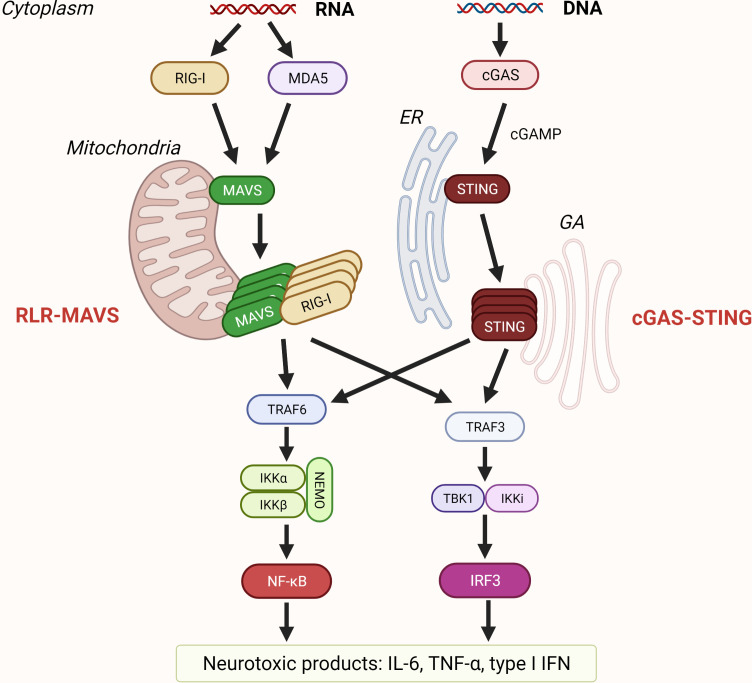
Figure 3.
Sensing of nucleic acids by RLR-MAVS and cGAS-STING pathway. Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) are RIG-I-like receptors (RLR) that recognize cytosolic dsRNA and ssRNA. RLR filaments that form CARD tetramers associate with the CARD domain of mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) that is localized on the mitochondrial membrane and trigger its polymerization. Recruitment of TRAFs results in activation of transcription factors interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). Cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS) is a cytosolic dsDNA sensor, and when activated, cGAS catalyzes the formation of cGAMP that binds to stimulator of interferon genes (STING) residing on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Upon oligomerization, STING traffics from ER to Golgi apparatus (GA) leading to activation of transcription of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) TNFα, and type I interferons (IFN).