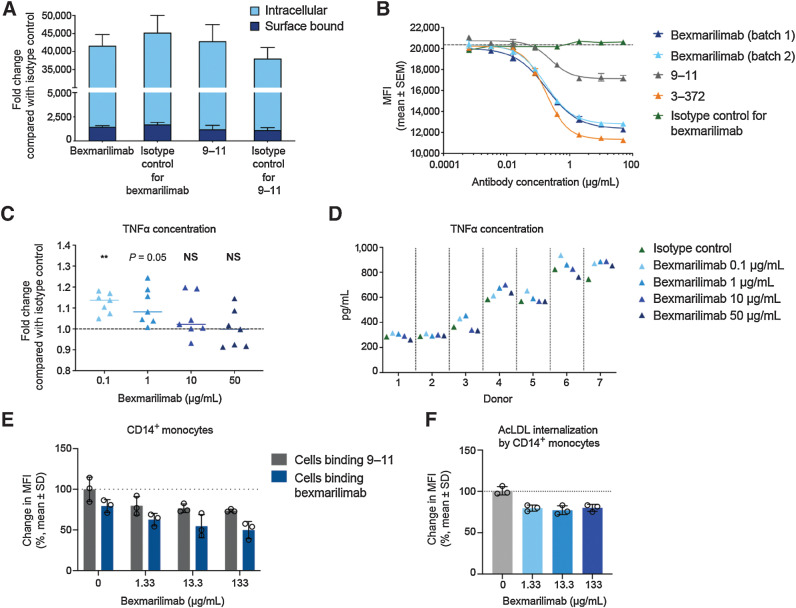
Figure 2.
Bexmarilimab binds to Clever-1 on monocytes and inhibits internalization of acLDL while inducing TNFα secretion. A, Internalized and surface-bound S. aureus particles in monocytes from healthy human donors after treatment with bexmarilimab, mAb 9–11, or their respective isotype controls. B, Internalization of acLDL into KG-1 cells via Clever-1 receptor in the presence of two batches of bexmarilimab, mAb 9–11, parental mouse antibody 3–372, and an isotype control as determined by a competition assay and flow cytometry. The dotted line indicates the level of internalization without a competitor compound present. C, Mean fold changes in TNFα secretion by primary human macrophages upon treatment with 0.1–50 μg/mL bexmarilimab compared with an isotype control. The macrophages were induced in vitro from CD14+ monocytes obtained from seven healthy donors. **, P < 0.01; NS, not significant compared with isotype control. The statistical analysis was performed using one-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett test. D, Absolute levels of TNFα secretion by primary human macrophages (C) upon treatment with 0.1 to 50 μg/mL bexmarilimab or an isotype control. Each donor is shown separately. E, Whole blood from 3 healthy donors was incubated with bexmarilimab or Ig-control for 24 hours at concentrations of 1.33, 13.3, or 133 μg/mL. These correspond to the initial estimated concentrations after injection of the antibodies into a blood volume of 4.5 L at doses of 0.1, 1, or 10 mg/kg, respectively, in a 60-kg person. Receptor occupancy of bexmarilimab on human CD14+ cells was measured by flow cytometry. The binding of fluorescently labeled bexmarilimab on CD14+ cells after administration of nonlabeled bexmarilimab is shown in blue and the binding of fluorescently labeled 9–11 antibody is shown in grey. Data normalized to Ig-treated cells. F, Flow cytometry analysis of acLDL internalization in CD14+ cells after bexmarilimab treatment (E). The blood was spiked with 1 μg/mL of AF488-acLDL during bexmarilimab incubation. Data normalized to Ig-treated cells.