Figure 3. Mechanisms in the TSS pathway that regulate cystine deprivation-induced ferroptosis independent of de novo cysteine synthesis and GSH.
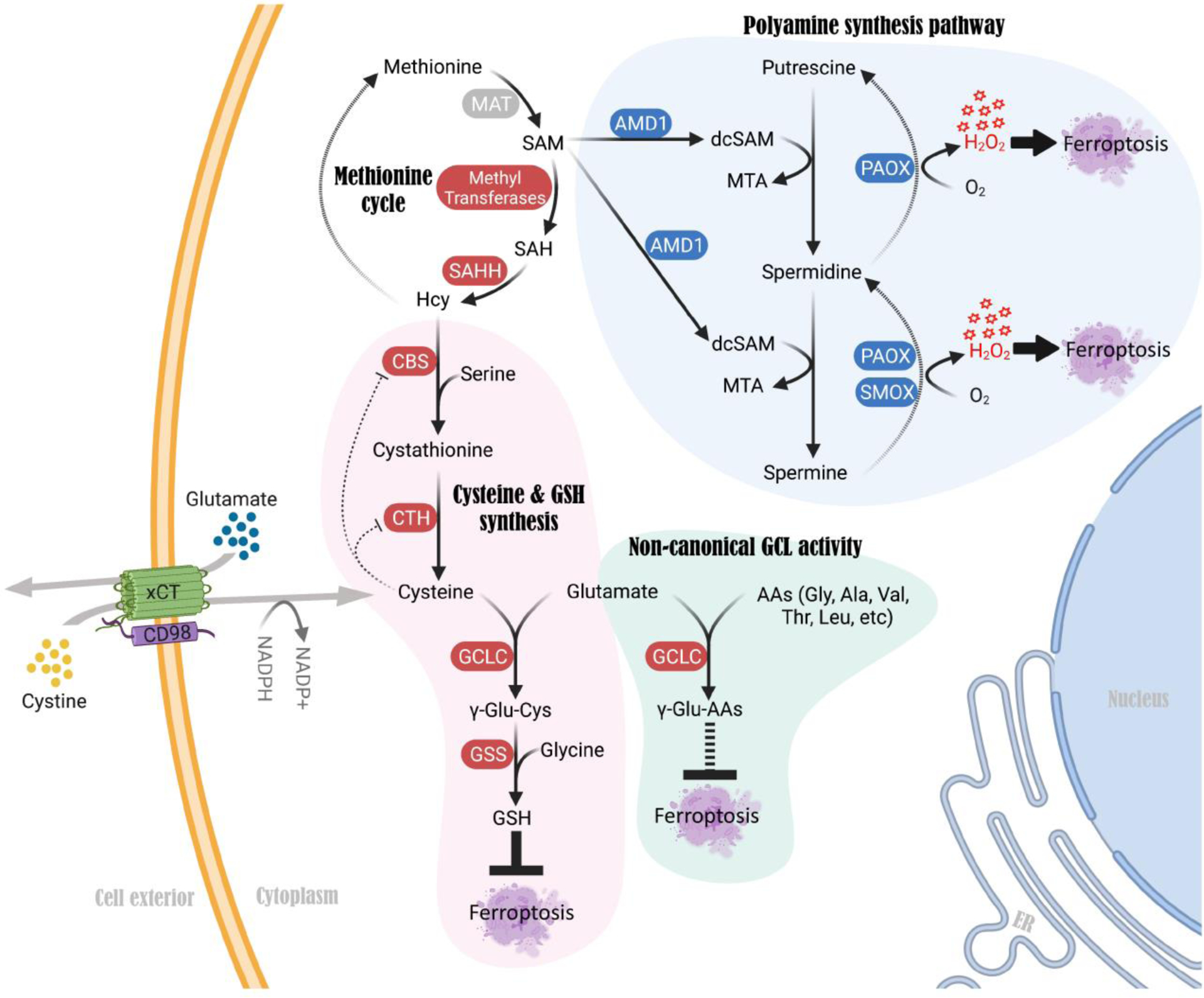
A non-canonical function of GCLC, an enzyme that is known to catalyze γ-glutamyl-cysteine formation during GSH synthesis, mediates γ-glutamyl-peptide synthesis upon cystine deprivation. This non-canonical mechanism alleviates glutamate stress and prevents cystine starvation-induced ferroptosis in cancer cells. Genetic or pharmacological blockade of GCLC sensitizes cancer cells to cystine deficiency-induced ferroptosis. In contrast, activation of the polyamine synthesis pathway downstream of methionine promotes ROS (H2O2) production, which triggers cell death upon cystine starvation. Blocking each of the key enzymes in the polyamine synthesis pathway, such as AMD1, PAOX and SMOX, alleviates ROS levels and protects cells from cystine starvation-induced ferroptosis. Abbreviations: GCLC, Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GSS, Glutathione synthetase; AMD1, Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase 1; PAOX, Polyamine oxidase; SMOX, Spermine oxidase; dcSAM, decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine.
